It has been a long time since fiber optic broadband became a viable network solution. More recently, however, it has become increasingly accessible and popular with home users. Fiber optic connections offer better performance in terms of speed and bandwidth than copper connections. This article discusses the applications, types and functionality of fiber broadband connections.
What is fiber optic broadband? How does it work?
Fiber optic broadband is a type of Internet broadband connection that uses optical fibers. These optical fibers transmit data in the form of light. In comparison, conventional copper cables use electrical signals for data transmission.
Light signals are transmitted in an optical fiber using total internal reflection (TIR). Total internal reflection is a phenomenon in which light rays are reflected when they leave one medium and enter another, as different materials have different densities.
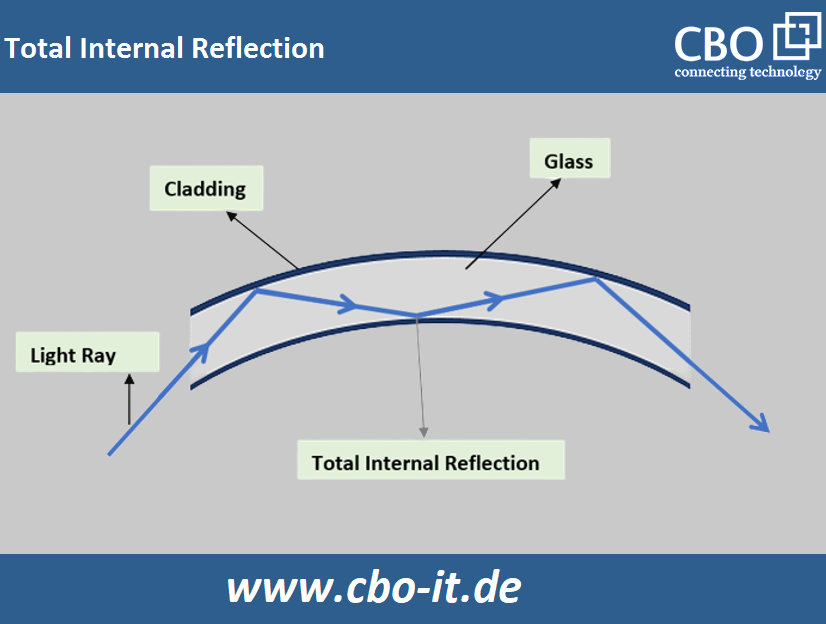
In optical fibers, the light that passes through the core of the fiber is totally reflected as it approaches the boundary where the glass (faster medium) and cladding (slower medium) meet. In this context, it is important to understand that total internal reflection causes no loss, whereas energy is lost during normal reflection. This is why we use TIR in fiber optic cables.
Fiber optic broadband - types
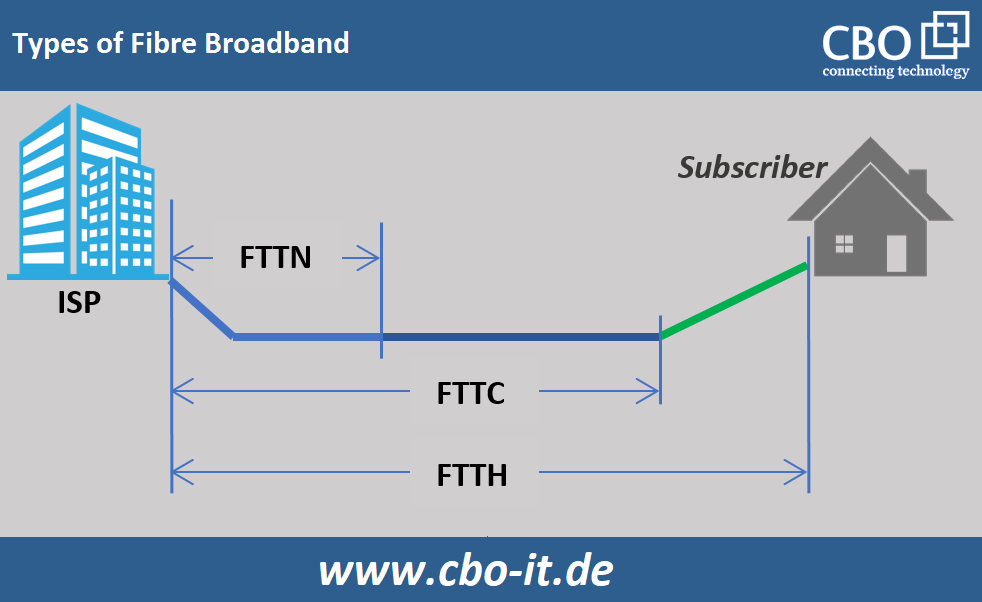
FTTP oder FTTH
These stand for fiber-to-the-premises or fiber-to-the-home. This type of broadband offers maximum speed, as we get the Internet and other services directly to our premises or home via the fiber optic cable.
FTTC
The abbreviation for FTTC is fiber-to-the-curb. In this scenario, a fiber optic cable from the Internet provider reaches a curb or pole near our property. From this distribution point, we receive the Internet and other services via a coaxial cable. So in FTTC networks, we provide services over a mix of traditional and fiber infrastructure.
FTTN
FTTN means fiber-to-the-neighborhood. With this type of broadband network, the ISP lays a fiber optic cable from its data center to a node in any neighborhood. All subscribers in the community receive services from this node via a coaxial cable. FTTN is the slowest type of connection. With FTTN, the speed of the network and the quality of service depend heavily on the distance between our premises and the node.
Fiber optic broadband compared to wireless broadband
Fiber broadband has many advantages over wireless broadband. As we all know, wireless signals are transmitted in different frequency bands that often overlap, leading to a degradation in the overall performance of the network. Another problem with wireless broadband networks is that wireless signals tend to be weaker because they are absorbed by buildings, trees and other obstacles.
In contrast, light signals transmitted in separate fiber optic cables can never overlap and are not affected. Therefore, fiber optic broadband is the better choice in terms of reliability and speed, so we can use it for long-term communication.
In terms of network security, fiber internet or fiber broadband offers better protection. Wireless broadband networks remain vulnerable to outside attacks. An attacker can easily identify your wireless network and penetrate the network using software or hardware resources. At the same time, no one can penetrate your network without having physical access to a fiber optic connection.
Fiber optic broadband - Applications
Telecommunications companies use fiber optics for the transmission of cable television, telephone and internet. However, there are countless applications for fiber optic broadband, such as;
- Game streaming: Streaming high-quality video via coaxial cable is possible. However, for game streaming or online gaming, we need fast fiber broadband connections. Fiber broadband connections can handle higher online gaming better as they offer faster download speeds and low latency. Low latency is crucial for streaming games as players can see the reaction to their actions as well as the reaction of their gaming partners immediately on the screen.
- Telemedicine: Telemedicine is a revolutionary innovation in the healthcare sector. You can now consult your doctor via a high-quality fiber optic broadband connection.
- Working from home: Many of us were unfamiliar with this concept before the pandemic. However, working from home is not new, as it existed before the pandemic. Today, people working in multimedia, graphic design, web engineering and other bandwidth-intensive fields can also offer their services via fiber optic broadband connections while staying at home.
Fiber optic broadband - advantages for companies
The ultra-fast and reliable fiber optic broadband network offers both private and business users various advantages, e.g;
- The high speed offered by fiber broadband Internet has a positive impact on employee productivity, which in turn translates into better service performance and more customers.
- Companies that have fiber broadband have less downtime and network disruption. More reliable networks mean better processes and consequently better results.
- Workplaces connected via fiber broadband can communicate more efficiently with the outside world. Sharing resources, video conferencing and seminars are no longer a problem with fiber broadband.
- Coaxial networks are not suitable for modern, IoT-based applications as they cannot cope with latency. Fiber broadband, on the other hand, offers very low latency and allows users to collaborate on projects in real time.
Fiber optic broadband - FAQs
Fiber optics vs. broadband - which is better?
Fiber optics and broadband both stand for completely different network concepts. Broadband refers to an Internet connection (and other services) with a high bandwidth. On the other hand, the term fiber optic is generally used for optical cables.
Optical cables are one method of providing broadband internet services to the subscriber. However, it is not the only option as there are also wireless and DSL broadband connections. However, fiber broadband is the best solution for the last mile in terms of speed and reliability.
Fiber broadband uses optical fibers to transmit and receive information via light waves. DSL broadband networks use copper cables, while wireless broadband networks transmit data via radio waves.
What is fiber optic broadband?
Fiber optic broadband is a high-speed technology that uses optical fibers for data transmission. There are three types of fiber broadband: FTTN, FTTC and FTTP. Each of these types refers to the extent to which fiber optic cables are used per connection.
FTTP connections offer the best network speed, as the maximum distance per connection is covered by one fiber optic cable. In contrast, FTTN falls into the third category, as these connections use a fiber optic cable between the ISP's data center and a shared node that serves many subscribers.
Do I need a fiber optic broadband router?
Yes, we cannot access our fiber optic broadband connection without a router. This is because the fiber optic cable transports data and routers ensure that users receive the relevant data. If you have subscribed to an FTTN or FTTC broadband connection, your normal router can take over this task. However, FTTH or FTTP subscribers need a router that can work with the ONT (Optical Network Terminal). ONTs work similarly to traditional modems, but are capable of receiving light signals and converting them into electrical signals. In general, the ISP provides its subscribers with the necessary hardware components. Today, there are 2-in-1 type ONTs that also have integrated routing functions.
Conclusion
Driven by the extraordianary demand for gigabit and 10-gigabit broadband, the deployment of fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) or fiber broadband is expected to reach record numbers in the coming years.
In FTTH deployment, the entire network connection between the ISP's servers and the user's premises is established via a fiber optic cable. Fiber broadband connections offer more speed, bandwidth and lower latency than traditional copper connections. To really take advantage of fiber networks, you need to prioritize FTTH over FTTC and FTTN.
 English
English
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 Espaniol
Espaniol