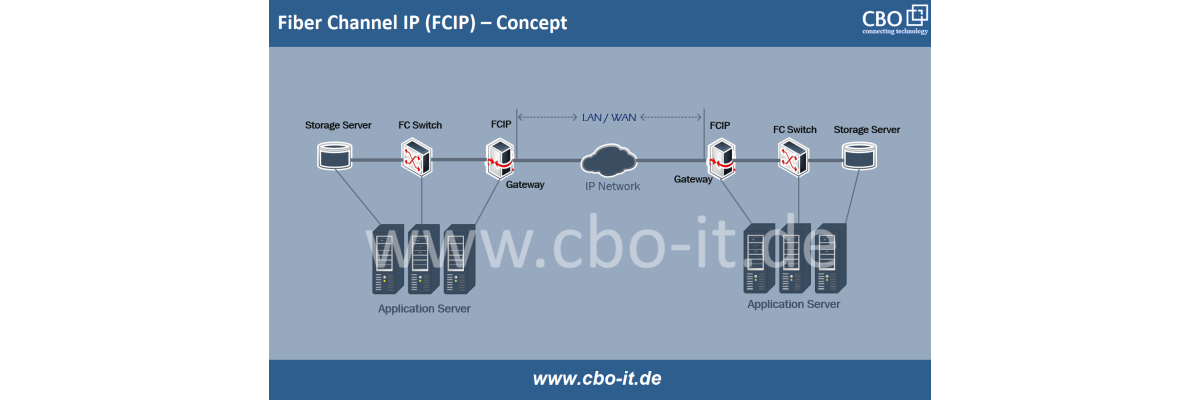
The 100G technology is a network data transmission technology that allows speeds of up to 100 gigabits every second. Its speed is much higher than the previous class, hence is enough to cater to the ever-growing need for bandwidth in data centers of the clouds, telecommunications, and networks within enterprises. 100G operates in different form factors and uses modulation schemes, making use of more than one wavelength or lanes of data to reach the intended bandwidth. This is often mitigated through the use of techniques such as PAM4 (Pulse Amplitude Modulation with 4 levels) or CWDM (Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing) technology.
Types of 100G Transceivers
Different kinds of 100G Transceivers, made according to the needs of distance, fiber, and type of network, are mainly:
- 100GBASE-SR4: Uses multimode fiber for short-range up to 100 meters, ideal for data center interconnects.
- 100GBASE-LR4: Single-mode fiber, 10 km, best for longer intra-city links.
- 100GBASE-ER4: Extends reach up to 40 kilometers over single-mode fiber, used in metropolitan networks.
- 100GBASE-PSM4: Utilizes parallel single-mode fiber for up to 500 meters, often chosen for data center use.
- 100GBASE-CWDM4: Utilizes the CWDM technology over single-mode fiber for distances up to 2 km, wherein it quite effectively balances reach with the occupation of bandwidth.
Common 100G Breakout Applications
In breakout applications, it enables the possibility of breaking down a single high-capacity link into several low-capacity ones, giving the network manager flexibility in his design and use of the network. Below is a description of a 100G transceiver and its potential in breakout scenarios.
- 100GBASE-SR4: Breakout to 4x 25G connections, supporting server connection to Top-of-Rack (ToR) switches in a data center LAN.
- 100GBASE-PSM4: Supports the breakout to 4x 25G links in aggregating server traffic and/or allowing connection to multiple devices at 25G rates.
- 100GBASE-LR4 and CWDM4: In less common use, it finds applications where its use is required for the link specialist at lower-speed links over extended range, as these can break out technically into 4x 25G connections.
It is really important to make sure that, in breakout applications, the transceiver, host device, breakout cable, or adapter are all designed to be compatible and meet the requirements for maintaining the signal and performance.
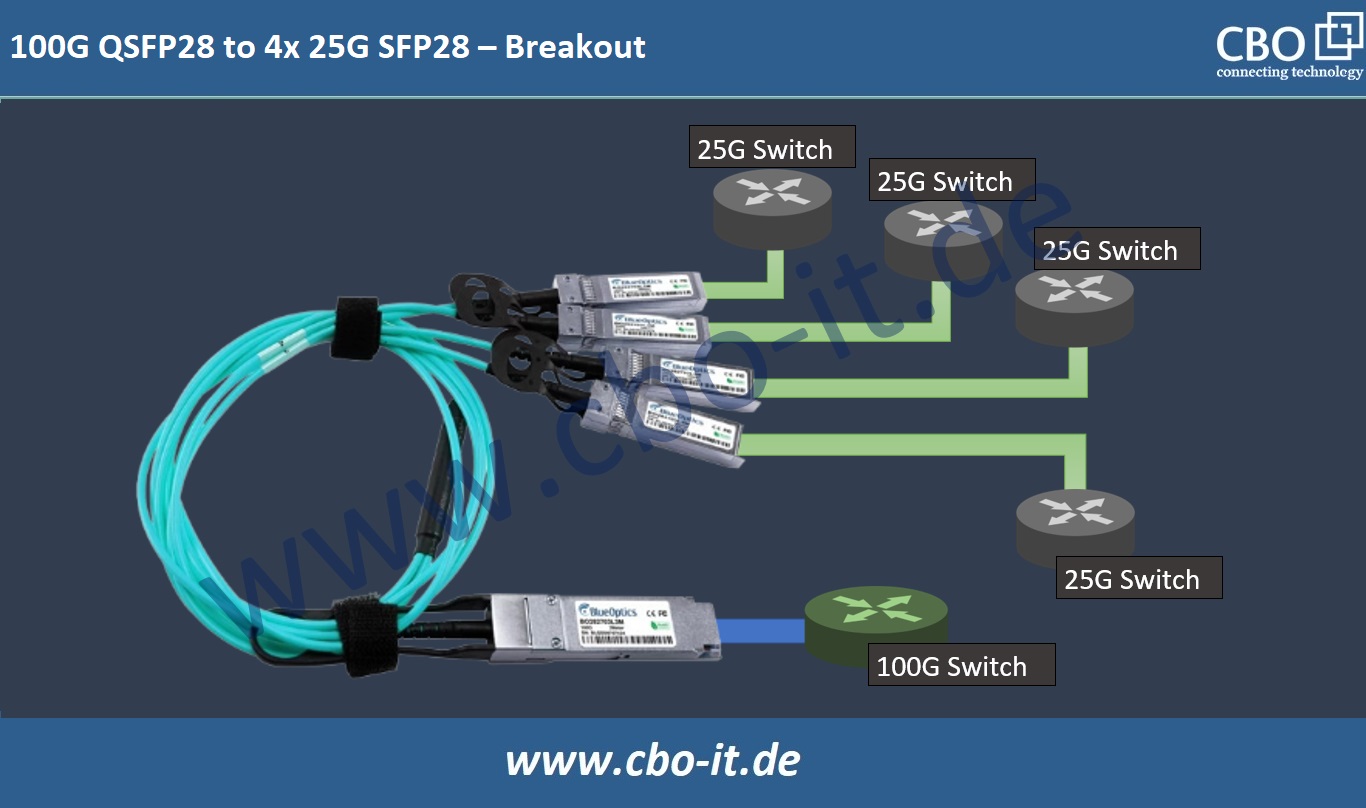
Breakout configurations in the data center are beneficial in optimizing port utilization on switches and routers, allowing an efficient and scalable network design.
100G Compatible Connectors
The choice of the connectors for 100G applications needs to be critical, having in mind signal integrity, the ease of use during connection, and general performance of the network. Common with 100G Transceivers and their cabling systems are the following types of connectors:
- MTP/MPO: It is a multi-fiber connector used in supporting various fiber counts and is normally used with 100GBASE-SR4 and 100GBASE-PSM4 transceivers. Particularly, connectors MTP/MPO work best for highly dense fiber systems, like data centers, as they allow 8 to 12 fibers to be plugged directly to aid the parallel optic transceivers.
- LC (Lucent Connector): LC is a small factor form fiber optics connector applied with both single and multimode fiber. Generally, they find applications in 100GBASE-LR4, 100GBASE-ER4, and 100GBASE-CWDM4 transceivers. The LC connector's small form factor offers high-density qualities and a compact design suitable for space-constrained environments
- SC (Subscriber Connector or Standard Connector): SC connectors have been widely used in fiber optic networks for many years and, while less common in 100G applications compared to MTP/MPO and LC connectors, they provide a robust and reliable connection
- QSFP28 Ports: QSFP28 (Quad Small Form Factor Pluggable 28) isn't really a connector but a port that provides for insertion with 100G Transceivers. QSFP28 ports host transceivers with LC or MTP/MPO connectors, according to the transceiver type.
Each connector type serves different network needs:
MTP/MPO Connectors: This would be most preferable for the data center, as the MTP/MPO connector supports short-distance, high-bandwidth parallel connections that carry parallel transmission for 100G and above.
LC Connectors: The LC connector will be very flexible and could cover every kind of short-to-long-distance 100G application with one or two channels executed in simplex or duplex configurations.
SC Connectors: SC connector and its pull-proof design offers good connection for those network applications which may not require either the density or latest speed standards, though they receive the same level of robustness as given in SC design.
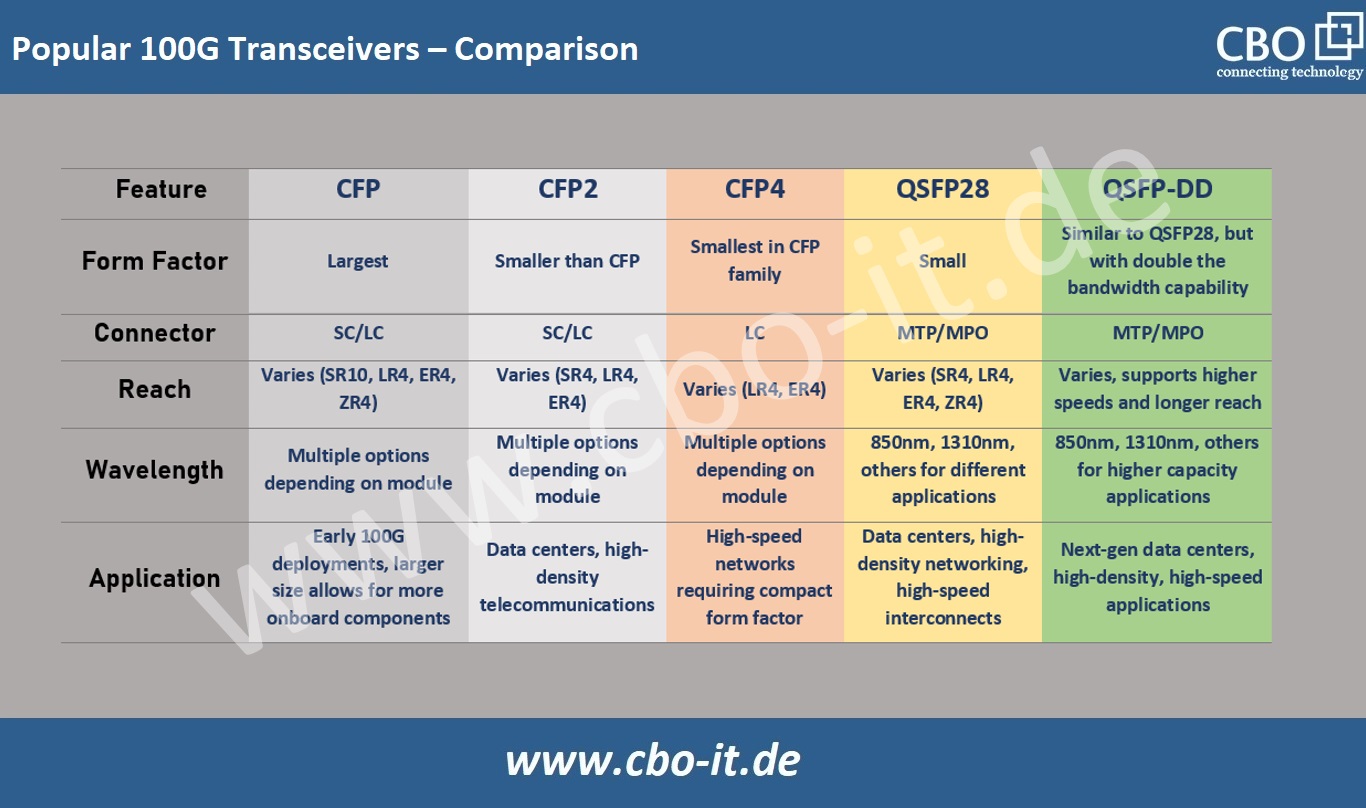
Popular 100G Transceivers – Comparison
The following exhibit summarizes differences between some of the most popular types of 100G Transceivers available on the market;
Conclusion
The 100G technology has been one of the major key milestones in the evolution of network capabilities in meeting the ever-growing higher bandwidth demand posed by modern digital infrastructures. From transceivers ideal for short-throw data center interconnect to the biggest data center transceivers for long-haul telecommunications, you're free to customize 100G networks for any connectivity environment. These make such networks more effective and powerful, using state-of-the-art modulation schemes such as PAM4 and multiplexing technologies like CWDM and DWDM.
The breakout applications also introduce flexibility in designing the network, thus achieving efficiency in port and cable usage through flexible connection strategies. Considering these connectivity options of MTP/MPO, LC, SC, and even QSFP28 ports as part of the configuration, it can be said that this is a system built around the performance levels of high-speed data transfer.
 English
English
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 Espaniol
Espaniol