In today's digitally connected world, internet access has become essential. However, not all internet connections are created equal. Different internet connection types vary in speed, reliability, availability, and technology. Understanding the differences between these connection types can help you make informed decisions when choosing the most suitable option for your needs. This article will explore the disparities between various internet connections, ranging from traditional dial-up to modern fiber optic connections.
Dial-Up Connection:
If you had access to the internet back in the 1990s, you must be well informed about dial-up connections. It was the only method available then. Dial-up connections use existing copper phone lines to send data to and from online servers. Dial-up connections are remembered as the slowest ones. Users must dial their ISP's number using a desktop or laptop computer's modem to establish a dial-up connection. Dial-up modems are obsolete these days. The most significant issues with the dial-up connection were limited bandwidth and the ability to use telephone lines without terminating your internet session. Dial-up connections are good for checking emails and for web browsing only.
DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) Connection:
Digital subscriber line connections also use ordinary copper telephone lines. However, DSL connections offer much higher speed and bandwidth than the dial-up ones. DSL connection performance can vary depending on the quality of the telephone line and the distance from the provider's central office. DSL is one of the most popular connection types in many developing countries as it's affordable and widely available. Deployment of DSL internet connections is relatively easy as it can work on the existing telephone infrastructure. Generally, ISPs provide DSL subscribers with Wi-Fi-capable MODEMs.
Cable Internet Connection
Cable internet connections employ coaxial cables, the cables used for cable TV transmission. Cable connections provide faster speeds compared to dial-up and DSL. They offer greater bandwidth, making them suitable for online gaming, video streaming, and large file downloads. However, cable internet speeds may fluctuate during peak usage due to shared bandwidth among users in a specific neighborhood.
Satellite Internet Connection
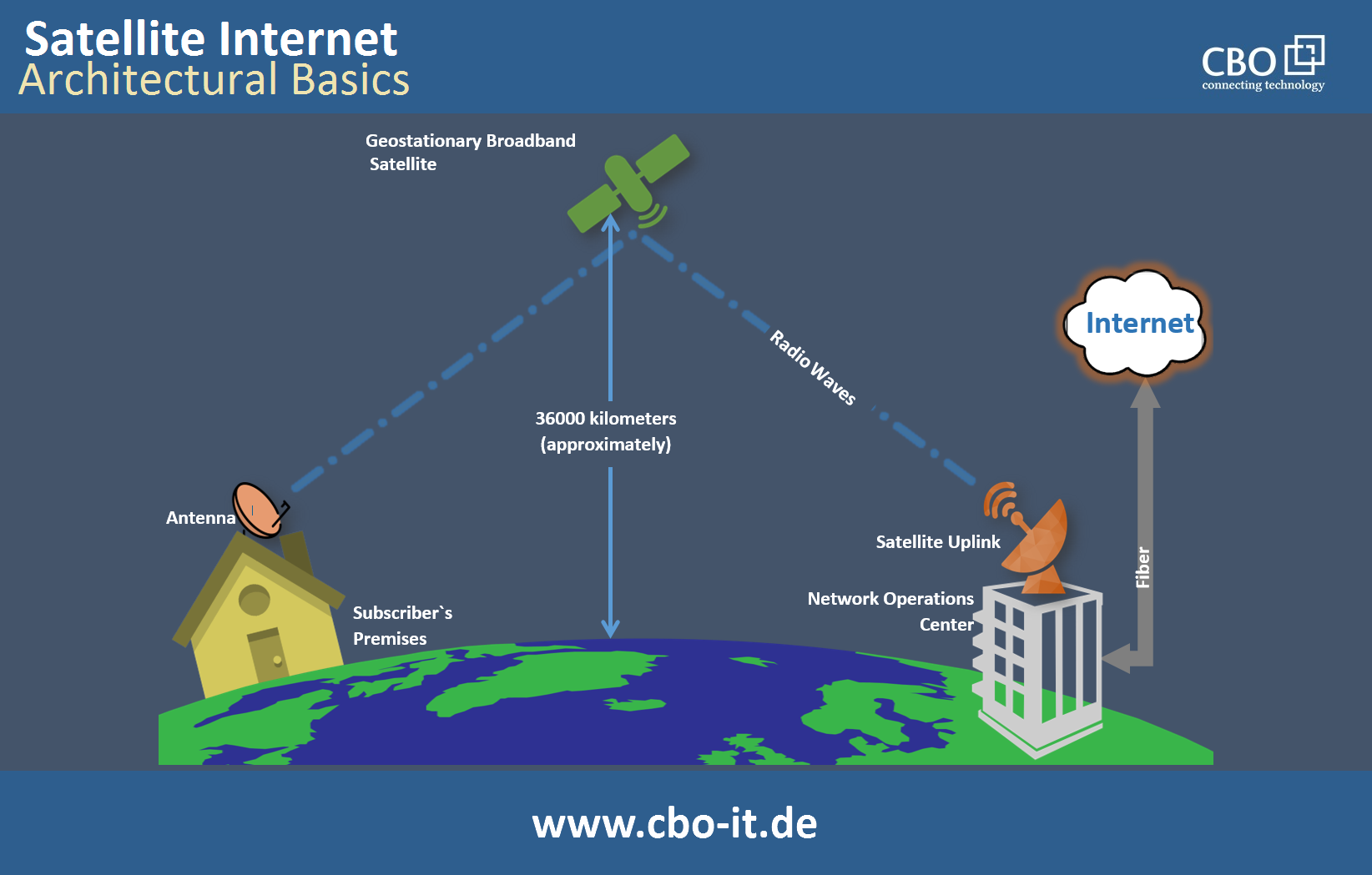
Satellite internet connections are viable for individuals residing in remote areas where terrestrial connections are unavailable. This technology relies on communication satellites to transmit and receive data signals. While satellite internet offers widespread coverage, it is typically slower and more susceptible to latency than other connection types. Weather conditions like heavy rain or snow can also interfere with signal quality.
Fiber Optic Connection
Fiber optic or optical connections utilize thin plastic or glass fibers to transmit data in light pulses. Optical fiber connections offer unmatched reliability, speed and with very low latency. These connections offer symmetrical download and upload speeds, making them ideal for bandwidth-extensive applications such as online gaming, streaming, and large-scale data transfers. The deployment of optical fiber connections increases exponentially as commercial and domestic users prefer fiber.
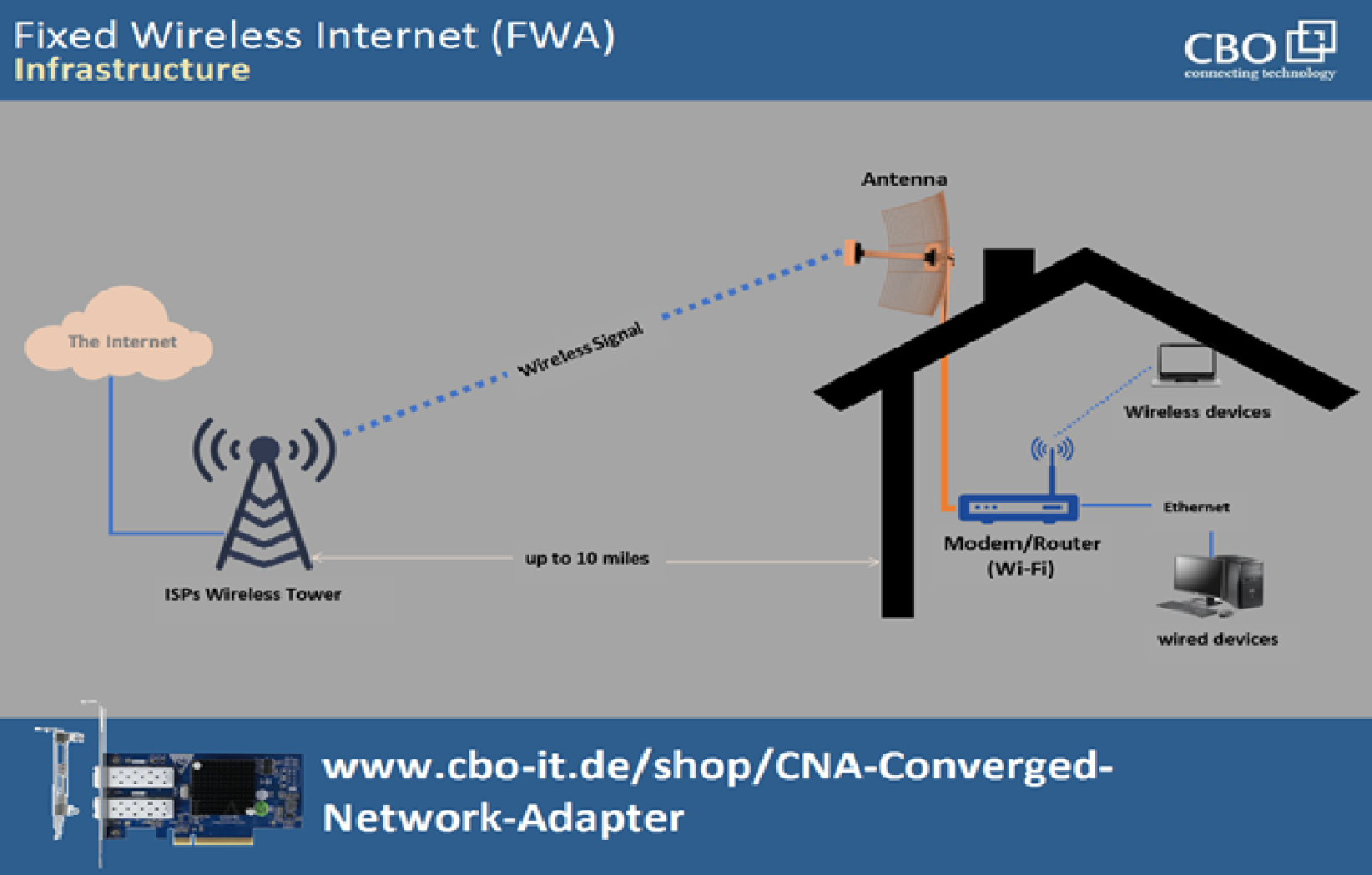
Fixed Wireless Broadband
In fixed wireless broadband setups, the ISP installs a receiver at an appropriate location on your property (usually on a rooftop) to let users from a fixed location access online resources through mobile networks. In these internet connections, data is transmitted through radio signals from the ISP's base stations, often mounted at cell towers. These base stations use backhaul connections to connect to the internet, and the backhaul connections are routed via point-of-presence. Fixed wireless broadband connections are ideal for locations without cable infrastructure, as they can help bring more population online quickly.
Typical Speeds by Connection Type
The typical speeds for each type of internet connection can vary. However, here is a general overview of the typical speeds for each type of internet connection:
- DSL speeds can range from 1 Mbps (megabits per second) to 100 Mbps for residential connections. However, the speed may depend on the distance from the provider's central office.
- Cable internet speeds can range from 10 Mbps to 1 Gbps (gigabit per second) or more, depending on the service plan. Cable connections are shared among users in the same neighborhood so that speeds may fluctuate during peak hours.
- Typical residential fiber speeds range from 100 Mbps to 1 Gbps or higher. In some areas with advanced fiber infrastructure, speeds up to 10 Gbps may be available.
- Typical speeds for satellite internet range from 10 Mbps to 100 Mbps. However, signal transmission latency or delay can be higher than other connections.
- Typical speeds for satellite internet range from 1 Mbps to 100 Mbps, with higher speeds available in areas with advanced fixed wireless networks.
Please note that these speeds are general estimates and can vary based on factors such as network congestion, the quality of the infrastructure, and the specific service plan you choose. It's always best to check with internet service providers in your area for the most up-to-date and accurate information regarding speeds available to you.
Average monthly Costs
The average cost of different types of internet connections can vary depending on factors such as location, service providers, and available plans. However, I can provide you with a general overview of the typical costs associated with each type of internet connection.
- DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) average monthly cost ranges from $20 to $60, depending on the speed and provider.
- Cable internet usually ranges from $30 to $100 monthly, depending on the speed and provider.
- Fiber optic internet tends to be more expensive. Depending on the speed and provider, it ranges from $40 to $150 monthly.
- Satellite internet prices can range from $50 to $200 monthly, depending on the speed and provider.
- Fixed wireless internet typically ranges from $30 to $100 per month.
It's essential to remember that these prices are approximate and may vary depending on various factors, including your location, the specific plans offered by internet service providers in your area, and any promotional offers or bundles available. It's recommended to check with local ISPs or service providers for accurate and up-to-date pricing information.
Conclusion
Internet connections have evolved tremendously from slow, sluggish dial-up to fast and reliable optical fiber. Today, DSL, Fiber, and Cable internet connection types are the most well-known and adaptive. Each type of internet connection has its limitations, pros and cons. A clear understanding of the differences between these connection types can help users make an appropriate decision based on reliability, speed, budget, and availability. The inception of 5G and other networking technologies has clarified that the journey is still ongoing, and we will have excellent connectivity options in the future.
 English
English
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 Espaniol
Espaniol