Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (or DWDM) and Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing (CWDM) are the two main types of wavelength division multiplexing that play a role in the context of optical transport networks (OTN). These WDM technologies can increase fiber bandwidth by combining (multiplexing) optical signals of different wavelengths on a single fiber strand. Although the basic working principle of coarse and dense wavelength multiplexing is the same, there are some differences. In this article, we will talk about CWDM and DWDM.
WDM, DWDM, CWDM basics
Before we compare CWDM with DWDM, it is better to know the basic introduction of WDM, CWDM and DWDM.
What is WDM?
WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexing) is a technology for data transmission between locations. With WDM, we can achieve more bandwidth by transporting data streams with different wavelengths over a single fiber optic cable. In this way, wavelength division multiplexing helps us to maximize the fiber utilization factor and optimize our network investments.
What is CWDM?
CWDM is a type of WDM. With Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing, a small number of channels are transmitted. It works with a wider spacing of 20 nm between the channels. This wider channel spacing makes CWDM less sensitive to temperature fluctuations. CWDM offers a maximum connection distance of up to 60 kilometers and was standardized by the IEEE for 10 Gigabit Ethernet back in 2004.CWDM is known for its flexibility, as it can be used in various fibre optic networks. In telecom access networks and corporate networks, CWDM is used for a point-to-point topology.
What is DWDM?
DWDM is a type of WDM. Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing transmits a higher number of channels. It works with a smaller distance of o.8 nm and 0.4 nm between the channels for 100 GHz and 50 GHz grids respectively. Due to the smaller distance between the channels, DWDM can be operated with a higher number of channels than CWDM. Another advantage of DWDM over CWDM is the possibility of amplification, which makes it an ideal choice for long-haul applications. When operating in a 50 GHz configuration, DWDM can provide up to 80 channels at 2.5 Gbps each. An unamplified DWDM link can provide a maximum link distance of 80 kilometers. With amplification, DWDM long-distance connections of up to 1000 kilometers can be realized.
CWDM vs. DWDM - What are the differences?
As already mentioned, both CWDM and DWDM are wavelength division multiplexing technologies. We use these two technologies to achieve the transmission of multiple signals with different data types over a single fiber. CWDM and DWDM are very popular and are considered practical tools to meet the increasing bandwidth requirements. However, there are some differences between the two technologies, the most common of which we will now discuss!
Distance between the channels
In wavelength division multiplexing, the channel spacing can be defined as the wavelength difference between two adjacent optical channels.
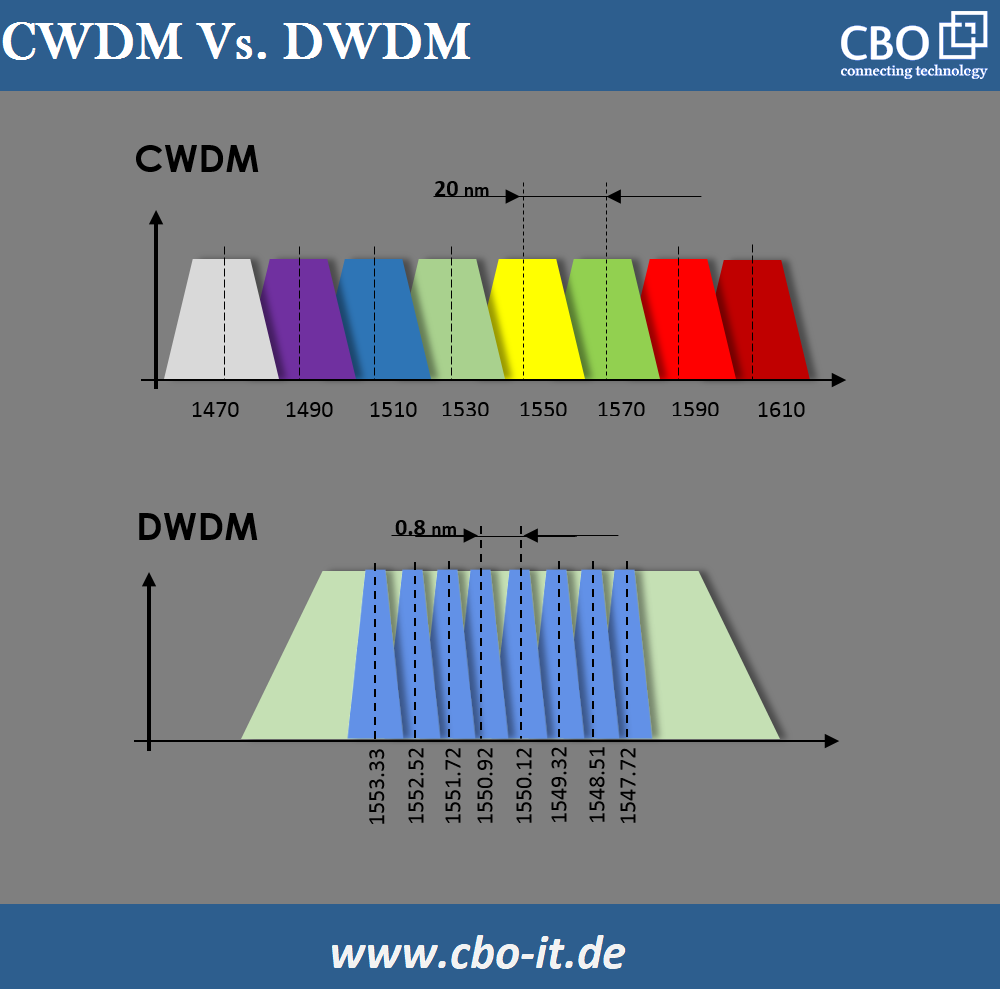
CWDM works with a larger spacing than DWDM and can therefore accommodate fewer wavelengths. To be more precise, with CWDM we can have a maximum of 18 optical channels with a channel spacing of 20 nm.
DWDM, on the other hand, works with a much smaller distance between the optical channels. This smaller spacing of 0.8 nm (for the 100 GHz raster) and 0.4 nm (for the 50 GHz raster) allows DWDM technology to handle up to 160 wavelengths. In typical scenarios, wavelengths from the C-band (1525nm to 1565nm) are used in DWDM systems, with the exception of some systems that can process wavelengths from the L-band (1570nm to 1610nm).
Transmission distance
CWDM is designed for short-distance communication, while DWDM is intended for long-distance communication. In CWDM systems, the channel spacing of 20 nm in the spectrum from 1470 to 1610 nm restricts the amplification, so that only a maximum connection distance of up to 80 km is possible.
On the other hand, as already mentioned, in DWDM systems, light streams of different wavelengths are transmitted with a much smaller channel spacing. In other words: In DWDM systems, many optical channels operate in a dense environment. Without amplification, a DWDM system can provide a maximum link distance of up to 120 km. The entire C-band spectrum used by a DWDM link can be amplified at low cost. With attenuation, a DWDM link can be optimized for many long-haul applications where links extend over hundreds of kilometers.
Optical modulation
CWDM and DWDM differ in terms of optical modulation. With CWDM, optical modulation is performed with electronic tuning and not with a cooled laser. With DWDM, on the other hand, the optical modulation is carried out with a cooled laser, whereby the tuning depends on the temperature. Although a cooled laser offers better performance, a longer service life and greater safety, it has the disadvantage of relatively high power consumption.
Cost factor
In terms of cost, CWDM generally offers a more cost-effective solution than DWDM. There are many factors that contribute to this cost difference, but the most important is the different type of optical components used. DWDM systems use complex cooled lasers, resulting in higher manufacturing and operating costs. In terms of installation and maintenance, CWDM systems are easier to install and maintain than DWDM systems. However, it is important to note that the cost difference should be evaluated based on the specific network requirements.
Advantages and disadvantages
As already mentioned, the main difference between CWDM and DWDM is the channel spacing of these two technologies. CWDM operates with a channel spacing approximately 100 times larger than DWDM. The channel spacing factor, along with several other factors, leads to specific advantages and disadvantages in terms of cost, performance, link distance, etc. Some of the main advantages and disadvantages of CWDM and DWDM are explained below.
CWDM pros and cons
Pros
- It consumes less electricity
- It requires less space
- Both singlemode and multimode optical fibers can be used
- It can use lasers or LEDs for power supply
- It works with cheaper and smaller wave filters
- It costs less and you can get started with less investment
Cons
- It offers less capacity than DWDM
- It has a shorter range
- Amplification is not possible
- Limited scalability is a disadvantage of CWDM
DWDM advantages and disadvantages
Pros
- It offers better capacity
- With EDFAs, DWDM can provide hundreds of kilometers of coverage
- Amplification is possible
- DWDM offers better scalability
- It offers more reliable data transmission over long distances
Cons
- More space is required
- Requires more power
- It can only work with high-precision wave filters and lasers
- EDFAs are expensive
- Implementation costs are much higher than CWDM
- DWDM systems can be very complex to install and maintain.
Conclusion:
CWDM and DWDM are two different optical communication technologies, each with their own advantages and disadvantages.
Choose CWDM if:
- Power efficiency and space saving are important factors.
- Your network is smaller or your budget is tighter.
- Amplification is not required and you are working in a shorter area.
Choose DWDM if:
- High capacity and long distance coverage are important requirements.
- Your network requires extensive amplification capabilities.
- You can allocate more physical space and power resources to the network.
- Precision and accuracy in wave filters and lasers are non-negotiable.
Ultimately, the decision between CWDM and DWDM depends on your specific network requirements, budget constraints and performance expectations. Evaluate these factors carefully to determine the most appropriate technology for your optical communications infrastructure.
 English
English
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 Espaniol
Espaniol