In the ever-evolving landscape of digital technology, the quest for faster, more reliable data transmission has led to significant innovations. Among these, optical USB cables stand out as a transformational advancement, redefining the boundaries of connectivity. This article delves into the world of optical USB cables, exploring their inception, technological nuances, and the profound impact they have on various sectors.
Introduction to Optical USB Cables
Since the introduction of Universal Serial Bus (USB) technology in the mid-1990s, USB has become the ubiquitous standard for data and power connections across countless devices. From its initial iteration to the latest USB4 specification, USB technology has continually expanded its capabilities, focusing on higher data transfer rates, increased power delivery, and greater versatility. Within this trajectory of innovation, optical USB cables have emerged as a groundbreaking development. Unlike traditional USB cables, which transmit data electronically, optical USB cables use fiber optic technology to transmit data as light, allowing for unprecedented data transfer speeds and longer cable lengths without signal degradation. The following exhibit contains a block diagram of USB 3.0 active optical cable;
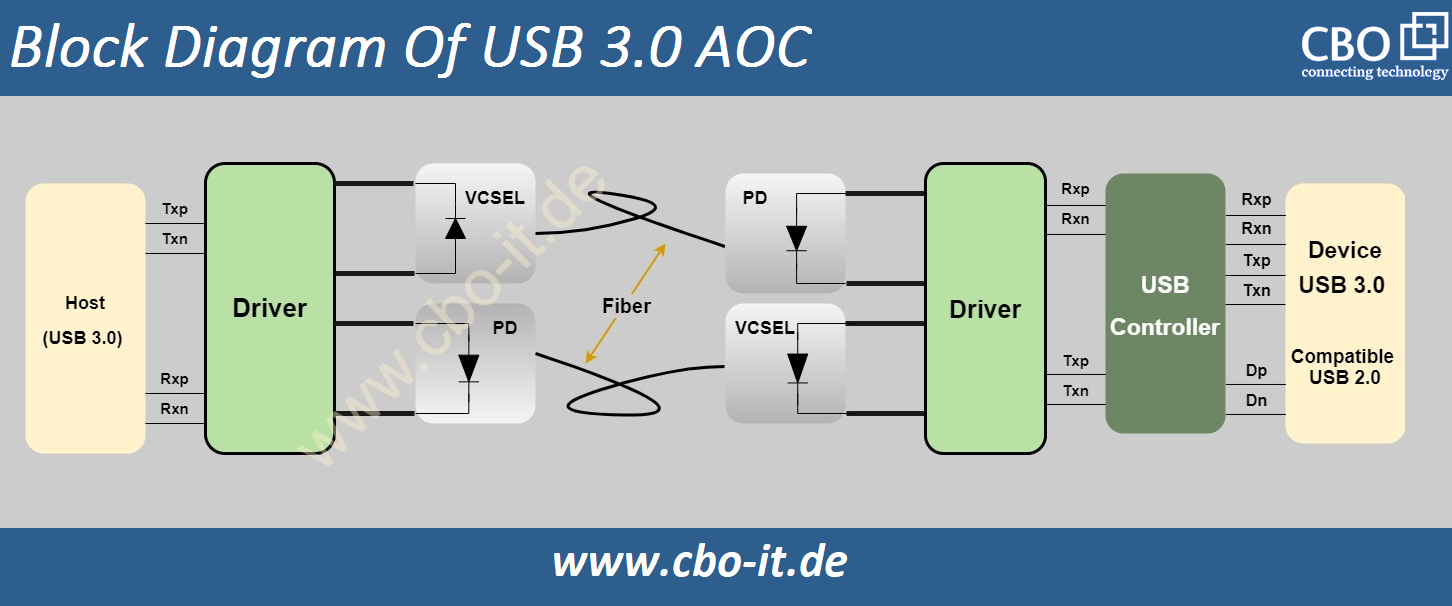
Technical Overview
Optical USB cables harness the principles of fiber optic technology, converting electrical signals into light pulses which travel through thin, flexible glass or plastic fibers. At the receiving end, these light pulses are converted back into electrical signals. This method of data transmission presents several advantages over traditional copper cables. For one, it eliminates issues related to electromagnetic interference, a common challenge for copper cables, especially in environments with numerous electronic devices.
Advantages of Optical USB Cables
The shift to optical USB technology offers several compelling benefits:
- Increased Data Transfer Speeds: Optical USB cables can achieve data transfer rates significantly higher than their copper counterparts, making them ideal for applications requiring the rapid movement of large data volumes.
- Longer Cable Lengths: One of the inherent limitations of copper USB cables is signal degradation over distance. Optical USB cables, however, can run for tens of meters without any loss in signal quality, expanding the possibilities for device placement and network configurations.
- Enhanced Durability: Being less susceptible to damage from bending and twisting, optical cables are more durable over their lifespan. Additionally, they are immune to electromagnetic interference, ensuring consistent performance in cluttered electronic environments.
Applications and Use Cases
The superior characteristics of optical USB cables have opened up new applications and use cases:
- In data centers and high-speed computing, where managing vast amounts of data quickly and reliably is paramount, optical USB cables provide an efficient solution.
- Audio/visual setups and gaming benefit from the high bandwidth and fidelity offered by optical cables, enhancing the user experience with seamless connectivity.
- Professional photography and video production sectors, where transferring large files without delay is crucial, also stand to gain from adopting optical USB technology.
Challenges and Considerations
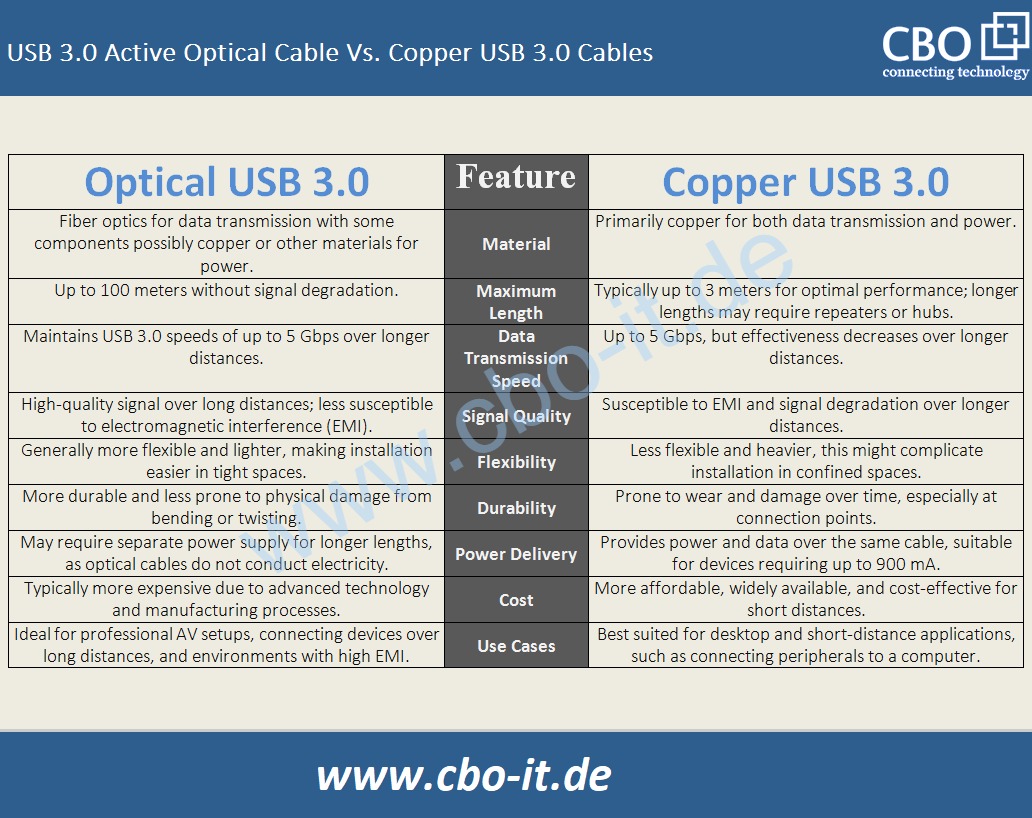
Despite their advantages, optical USB cables face challenges in terms of broader compatibility and market adoption. The higher production costs of optical cables, compared to copper, may deter some consumers and small-scale operations. Additionally, ensuring compatibility with existing devices and USB standards remains a hurdle for widespread acceptance. In the following exhibit you can find a quick comparison between Optical USB and traditional, copper USB cables;
The Future of Connectivity
Looking forward, the integration of optical USB technology is poised to play a significant role in the evolution of connectivity standards. As the demand for higher data transfer rates and more reliable connections grows, optical USB cables are set to become more prevalent in our digital infrastructure.
Which USB Standards Support Optical Fiber Technology?
Active Optical Cables (AOCs) are more commonly associated with USB 3.0 and later standards, such as USB 3.1 or USB3.2, primarily because these standards benefit significantly from the high data transfer speeds and extended cable lengths that AOCs provide. USB 3.0 and beyond support much higher data rates than USB 2.0—up to 5 Gbps for USB 3.0, compared to the 480 Mbps maximum of USB 2.0—making the need for AOCs more pronounced for applications requiring fast data transfer over long distances without signal degradation.
While it's technically possible to manufacture USB 2.0 Active Optical Cables, the demand for such cables is relatively low due to USB 2.0's slower data transfer rates, which can typically be accommodated with conventional copper cables without significant signal loss for the distances that USB 2.0 devices are commonly used. Therefore, the market for USB 2.0 AOCs is quite limited, and most AOC solutions focus on USB 3.0 and newer standards to take advantage of their speed improvements and applications that require high-bandwidth connectivity over longer distances.
In practical terms, when considering an upgrade to AOCs for enhanced performance, especially in professional or data-intensive environments, looking into USB 3.0 AOCs or newer would be more beneficial.
Conclusion
The evolution of USB technology, particularly with the advent of optical USB cables, underscores the continuous push for faster, more reliable connectivity solutions in various sectors. So, it can be concluded that;
- Optical USB cables represent a significant advancement in USB technology, promoting faster and more reliable connectivity.
- They challenge traditional data transmission constraints and enable new possibilities for device placement and multimedia applications.
- The transition faces hurdles like high costs and compatibility issues, impacting widespread adoption.
- Active Optical Cables (AOCs) are mainly associated with USB 3.0 and later, reflecting a shift towards high-bandwidth and long-distance data transmission.
- Their adoption and impact are poised to grow, driven by the demand for high-speed, reliable data transmission.
 English
English
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 Espaniol
Espaniol