Network hubs, once a staple for connecting devices on local area networks (LANs), have largely fallen out of favor due to advances in technology. While hubs still have some niche applications, they have several significant drawbacks that make them less practical in modern network configurations. This article examines the disadvantages of using a network hub.
Network hubs have a colorful past, as they were considered indispensable in local networks, and even today they are still very popular on a national level. However, in large, complex and powerful network applications, hubs are no longer considered an option. While hubs still work well for some segments, they have some significant shortcomings that make them less tangible, less practical and less secure in today's world where network security has become a major concern. In addition to the security factor, in today's world of bandwidth-intensive network applications such as high-definition video streaming, online gaming and cloud-based services, the limitations of a network hub become all too apparent. In this article, we'll talk about the main drawbacks of network hubs!
1. limited intelligence:
Hubs operate at the most basic level (i.e. the physical layer) of the OSI model, which means they require more intelligence than higher level network devices such as switches and routers. They cannot make scenario-based, intelligent decisions about where to route data packets because they cannot create and maintain an overview of the devices connected to their various interfaces.
2. emission of traffic:
Hubs are designed to send data packets indiscriminately to all connected devices. This leads to unnecessary network congestion as each device on the hub has to process and filter out packets that are not intended for them. This transmission of data packets can also create an insecure and easily infiltrated network environment.
3. inefficient use of bandwidth:
Since hubs transmit data to all connected devices, they use the available network bandwidth extremely inefficiently. This inefficiency can lead to packet loss, reduced performance, slower network speeds and other problems. Imagine playing an online game or streaming your favorite video while accessing the Internet through a network hub! That won't be a pleasant experience indeed.
4. lack of segmentation:
Unlike switches, which can divide an entire local network into multiple collision domains, hubs operate in a single collision domain. This means that when a device on the hub transmits data, it can collide with data from another device, resulting in a higher frequency of data collisions and therefore more retransmissions, more congestion and less efficient bandwidth utilization.
5. security risks:
One of the biggest shortcomings of hubs is the complete lack of even basic security features. Any device connected to a hub can easily eavesdrop on network traffic. Furthermore, just one infected device connected to a hub can cause damage to all other devices. Hubs are elementary devices that can be manipulated in many ways, especially if they remain physically accessible.
6. outdated technology:
Hubs have become obsolete in modern, advanced networks due to their many limitations. They don't even have the basic features needed to handle the complexity of today's network requirements.
7. limited scalability:
Scaling a network with hubs can be impractical. The more devices are added, the more collisions occur and network performance degrades further, leading to a reduction in available bandwidth and more congestion. Therefore, you cannot expand a network beyond certain limits by using only hubs.
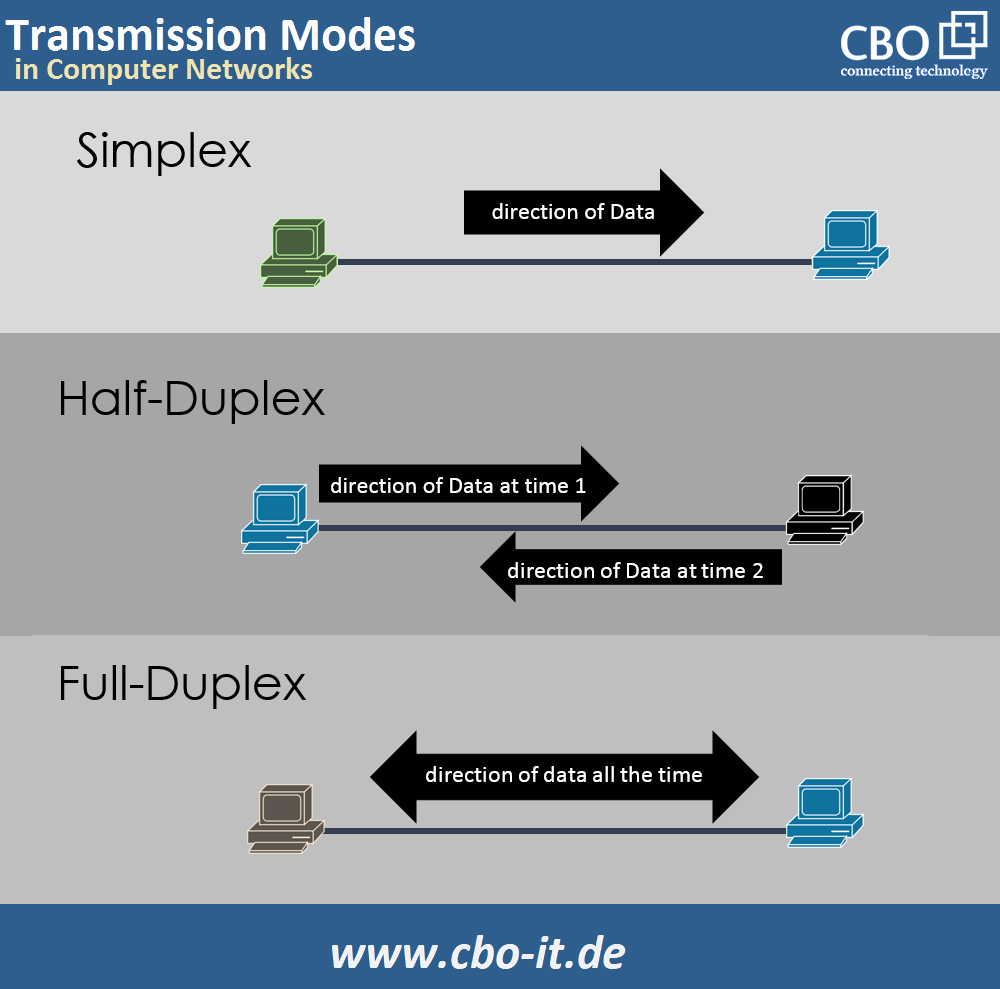
8. no support for full duplex:
Hubs unterstützen keine Vollduplex-Kommunikation, da sie ein Halbduplex-Kabel verwenden. Das bedeutet, dass Geräte, die an einen Hub angeschlossen sind, keine Zwei-Wege-Kommunikation gleichzeitig verarbeiten können. Switches und Router hingegen ermöglichen es den angeschlossenen Geräten, gleichzeitig Daten zu senden und zu empfangen. In der folgenden Abbildung wird zwischen den verschiedenen Übertragungsmodi in Computernetzwerken unterschieden.
Who else can benefit from networking hubs?
While the drawbacks of network hubs become apparent in larger, more complicated networks, there are still some applications where they can work. For home users and businesses with simple network requirements and modest budgets, network hubs may be sufficient to get the job done. In a small home network with only a few wired devices such as printers, scanners and a few desktop computers, the simplicity of a network hub's plug-and-play capability may outweigh its shortcomings. Similarly, small businesses that require basic connectivity between workstations may opt for a network hub before they have sufficient funds to invest in their network infrastructure.
Conclusion:
To summarize, while network hubs can find a place in basic network configurations or education, they are poorly suited for modern high-performance networks. Their lack of scalability, their inability to manage traffic efficiently and their potential security risks make them a less than ideal and unsafe choice for most network scenarios.
In today's technology landscape, switches have largely replaced hubs and offer more secure, intelligent and efficient solutions for building and managing networks. Finally, we would like to show you an example that enables a quick and easy comparison between hubs, switches and routers;
.png)
 English
English
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 Espaniol
Espaniol