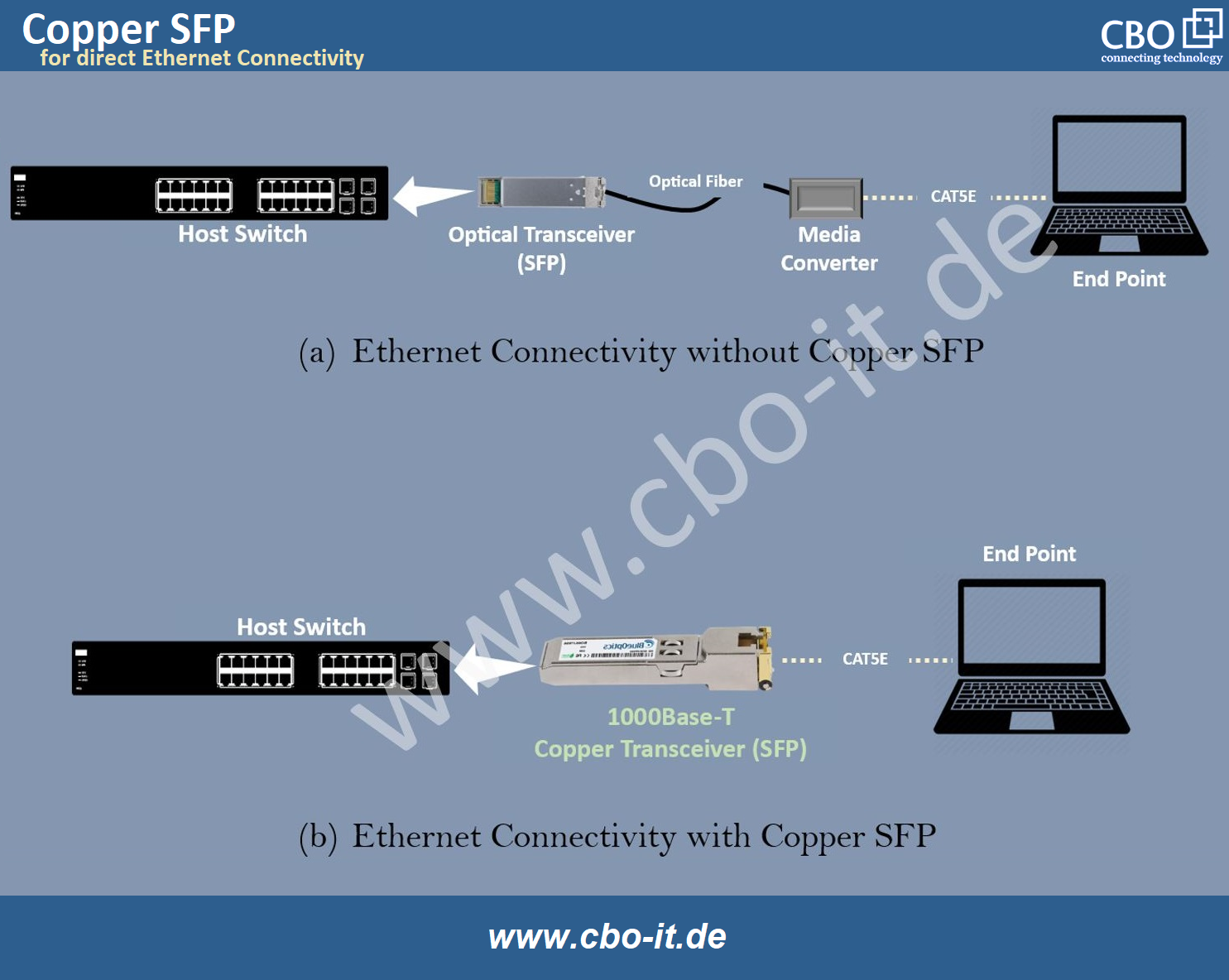
Optical transceivers or optical modules are essential devices that facilitate high-speed data transmission using optical fibers. They convert the electrical signals from networking equipment to the light waves that travel over fiber optic cables. On the other hand, we have copper SFP modules. These modules are considered a popular option for data-center-level, short-distance networking. Copper SFP or RJ45 SFP modules are widely used for achieving quick, reliable, and fast connectivity between routers, switches, and other networking equipment.
RJ45 SFP – Features
RJ45 SFP modules, called SFP-to-RJ45 transceivers, are compact and highly portable devices that facilitate connections between SFP ports over standard copper cables. They offer an affordable and flexible solution for extending network reach. Following are some of the most prominent features of Copper SFP modules!
Compact Size:
SFP modules comply with the SFP standard, providing a hot-swappable design that is a plug-and-play format that can be easily inserted into compatible network equipment.
RJ45 Interface:
The integrated RJ45 port allows direct use of standard copper Ethernet cables (mostly Cat 5e or Cat 6). Being one of the most widely used interfaces, the RJ45 brings almost unlimited possibilities.
1000BASE-T Connectivity:
These modules provide high-speed transmission for Gigabit Ethernet (1000 Mbps) over copper cable.
SFP Port Compatibility:
They are intended to be plugged into SFP ports of numerous network equipment such as switches, routers, servers, and media converters.
Copper SFP Module & its Types
Copper Small Form-Factor Pluggable (SFP) modules are essential components in networking, providing a versatile and efficient means of data transmission. Within Copper SFP Modules, various types cater to different networking requirements. This passage explores the critical types of Copper SFP Modules, shedding light on their distinctive features and applications.
10Base-T SFP:
Found at the lower end of the speed spectrum, 10Base-T SFP modules operate at a modest data rate of 10 Mbps. While considered relatively slow by modern standards, these modules play a crucial role in legacy networking environments where compatibility with older systems and equipment is essential. 10Base-T SFP modules provide a viable solution for scenarios focusing on basic connectivity rather than high-speed data transmission.
100Base-T SFP:
Among the foundational types of Copper SFP Modules, the 100Base-T SFP modules operate at a data rate of 100 Mbps. Commonly employed for Fast Ethernet connections, these modules provide a reliable and cost-effective solution for networks requiring moderate speeds. While slower than their Gigabit counterparts, 100Base-T SFP modules remain relevant in scenarios where higher data rates are not a primary requirement.
1000BASE-T SFP:
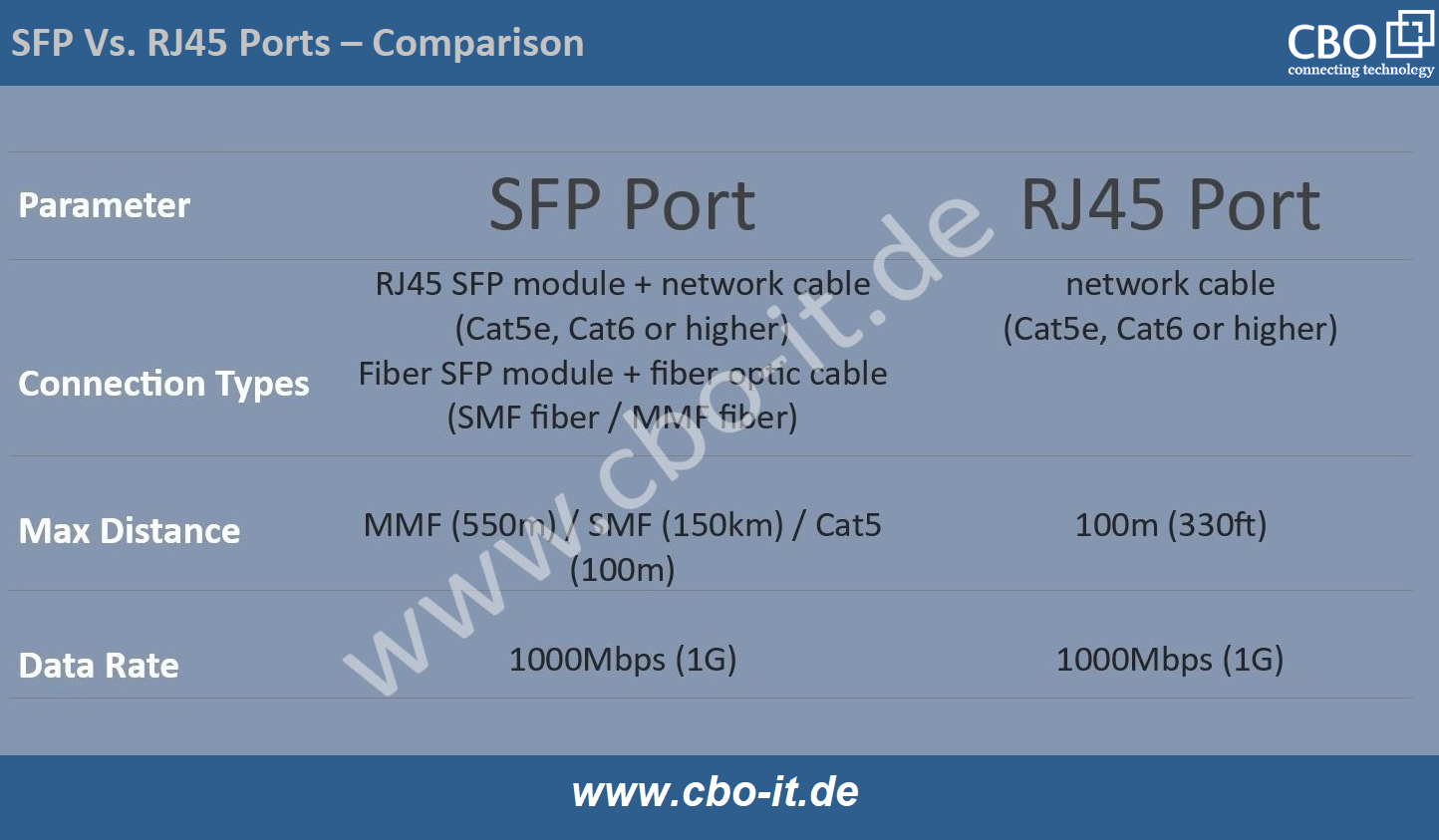
One of the most common types, the 1000BASE-T SFP modules, operate over Category 5 and 6 twisted pair cables. With a data rate of 1 Gbps, these modules are widely utilized for Gigabit Ethernet connections, offering cost-effective and reliable solutions for short to medium-range networking. The following exhibit offers you a quick comparison between various types of Copper SFP Modules;
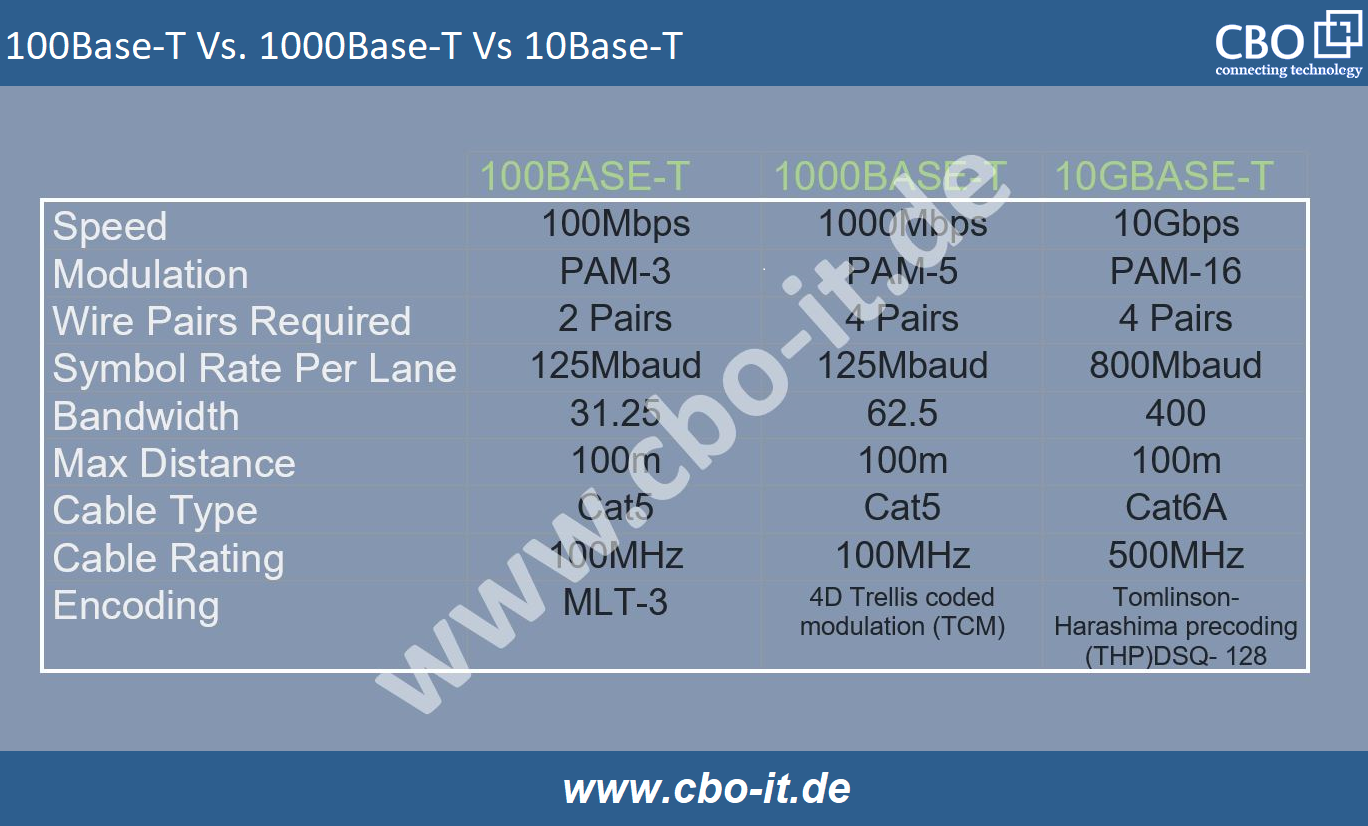
10/100/1000BASE-T SFP:
Designed for versatile compatibility, the 10/100/1000BASE-T SFP modules support multiple data rates, enabling seamless integration into networks with varying speed requirements. These modules automatically adjust to the optimal speed, providing flexibility for mixed-speed network environments.
10GBASE-T SFP+:
Stepping up to higher data rates, the 10GBASE-T SFP+ modules support 10 Gbps over copper twisted pair cables. Ideal for data centers and enterprise networks, these modules offer enhanced performance and bandwidth, extending the capabilities of copper-based connections to meet the demands of modern high-speed networking.
Copper SFP Module Applications:
Network Expansion and Upgrade:
- Increasing the number of ports on switches and routers without changing gear.
- Upgrading the existing network infrastructure to Gigabit Ethernet standards with readily available Cat5e/Cat6.
Data Center Interconnect:
- Allowing server-to-switch and switch-to-switch links in racks and within short distances inside data centers.
- It offers an inexpensive substitute to fiber optic SFP modules that can be used for inside rack and short-range interactive communication.
Point-to-Point Connections:
- Connect network devices in geographically dispersed locations within close range, such as across buildings or campus.
- Linking buildings a few hundred meters apart without using specialized fiber optic cabling or equipment.
Differences between Copper SFP and Optical SFP
Two main types of transceivers are employed in network installations: Fiber and copper Small Form-Factor pluggable (SFP) modules, which vary considerably. Both fiber and Copper SFP Modules are hot-pluggable transceivers used in network equipment, but they differ in several key aspects:
Interface:
- Fiber SFP Modules: These modules transmit data via optical fibers. They are usually LC duplex connectors with light signals (laser or LED).
- Copper SFP Modules: As opposed to the fiber SFP modules, copper ones feature cables constructed from copper material for data transfer. They are usually equipped with RJ-45 connectors, and their signaling occurs in the electric mode.
Cabling:
- Fiber SFP Modules: Fiber optics are a high bandwidth technology resistant to electromagnetic interference. Fiber cables are better as they have a small thickness and low weight and transmit signals over a considerable distance without the fear of signal shock.
- Copper SFP Modules: Copper cables are used in short distances. Copper cables used for short distances are more susceptible to electromagnetic interference, potentially affecting performance.
Use Cases:
- Fiber SFP Modules: High-bandwidth, long-distance transmission, and EM interference immunity require fiber optics to be used as the primary means. Some typical applications are data centers, the telecommunications industry, and building links.
- Copper SFP Modules: Copper modules are ideal for short-haul connections since the cost is essential. They are usually used for LAN connections inside the same rack or a building.
Transmission Medium:
- Fiber SFP: employs fiber optic cables consisting of ultra-thin glass fibers to send data as light pulses.
- Copper SFP: Conveys data by sending electrical signals over twisted-pair copper cables (such as Cat5e, Cat6, and so forth).
Transmission Distance:
- Fiber SFP: Provides much higher transmission distances by up to 120km and beyond, relying on particular fiber cable types and SFP modules as well.
- Copper SFP: The equipment is limited to shorter distances, 10 meters upwards to about a hundred meters, depending on the cable type and data rates.
Data Rate:
- Fiber SFP: Enables such speeds as 10Gbs, saving up to and including 40 Gbps, depending on the type.
- Copper SFP: Generally restricted to slow data rates, at most 10 Gbps, though a few can attain up to and beyond 25Gbps or even as high as 40Gbps within shorter distances.
Cost:
- Fiber SFP: Highly costlier than Copper SFP Modules because of the advanced technology used.
- Copper SFP: Less expensive, making them a budget-friendly option for short hauls.
Power Consumption:
- Optical SFP Modules: Optical SFP modules generally exhibit lower power consumption, making them a favorable choice for energy-efficient networking setups.
- Copper SFP Modules: Copper SFP Modules, while often more power-hungry than their optical counterparts, remain efficient for short-distance connections with moderate power demands.
Conclusion
In conclusion, RJ45 SFP modules are:
- Crucial connectors for bridging copper and fiber optic networks.
- Offering compact design.
- Affordability.
- Compatibility with standard Ethernet cables.
Understanding the diverse types of Copper SFP Modules, their applications, and the distinctions from Optical SFP modules empowers network professionals to make informed choices tailored to specific requirements. Whether prioritizing cost-effective short-haul connections or embracing the high-speed, long-distance capabilities of fiber optics, the decision between Copper and Optical SFP modules hinges on factors like distance, bandwidth, and environmental considerations.
 English
English
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 Espaniol
Espaniol