Foreword
In data centers, 100G QSFP is considered as the dominant form factor for 100G Ethernet. Various 100G interfaces are developed to satisfy a broad range of applications. The increasing popularity of 100G Ethernet is pushing Ethernet users to upgrade their existing 10G infrastructure to 100G. In this article we are going to discuss two specific QSFP28 based transceivers; CWDM4 and PSM4 and differences between them.
100G: Current Market Scenario
Currently, several 100G transceivers are available on the market including; CXP, CFP, CFP2, CFP4, and QSFP28. However, QSFP28 is the most celebrated one among them as it comes with a small form factor and consumes less power. SR4, LR4, SR10, and ER4 are IEEE defined transceivers available today. On the other hand, 100G CWDM and 100G PSM are two non-IEEE defined interfaces. The industry is expecting that these two interfaces are going to be a compelling alternative for 100G Ethernet. A quick comparison between the available 100G transceivers can be obtained from the table below:
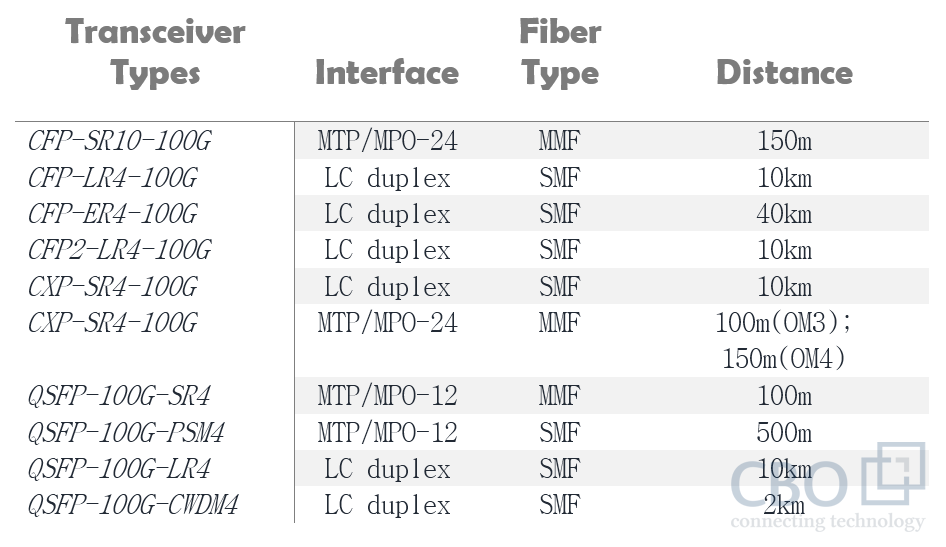

Why We Need 100G QSFP28 PSM4 and CWDM4?
As we know, 100G SR4 and 100G LR4 are fundamental 100G interfaces used today. These two interfaces are IEEE defined. However, for practical data center applications, their reaches are either too long or too short. Moreover, the 100GBASE-LR4 costs more. For data center operators 100G QSFP28 transceivers with 500 meters or 2 kilometers maximum reach are better choices. Here comes the role of MSA (Multi-Source Agreement) strategy. 100G QSFP28 modules with CWDM4 and PSM4 interfaces are two great products of the MSA. Their deployment costs much less than the 100GBASE-LR4 modules, and both of them are designed to offer distances beyond 100GBASE-SR4 QSFP28.
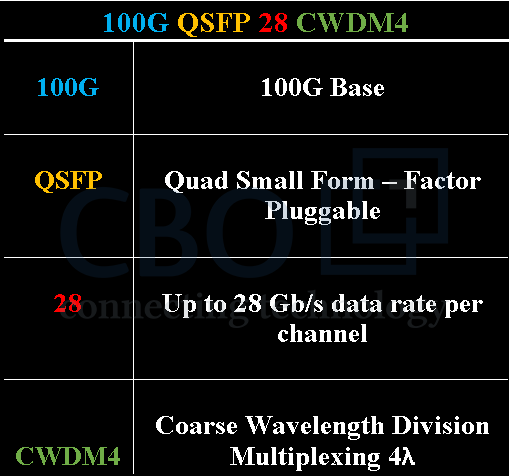
Introduction to CWDM4 Transceiver
The CWDM4 optical transceiver offers a 100G Ethernet link with a maximum allowed transmission distance of around 2 kilometers. CWDM4 is designed to interface with LC duplex connectors and uses 4 x 25 Gbps to provide 100 Gbps. In this transceiver four lanes with 1271, 1291, 1311 and 1331 nanometer center wavelengths are controlled on the transmission side. Whereas, four tracks of optical data streams operate on the receiver side. An integrated de-multiplexer is used to de-multiplex the receiving end data streams. We require a duplex SMF (single-mode fiber) only to connect 2 x 100G CWDM4 transceivers because of the availability of integrated optical multiplexer as well as optical de-multiplexer.
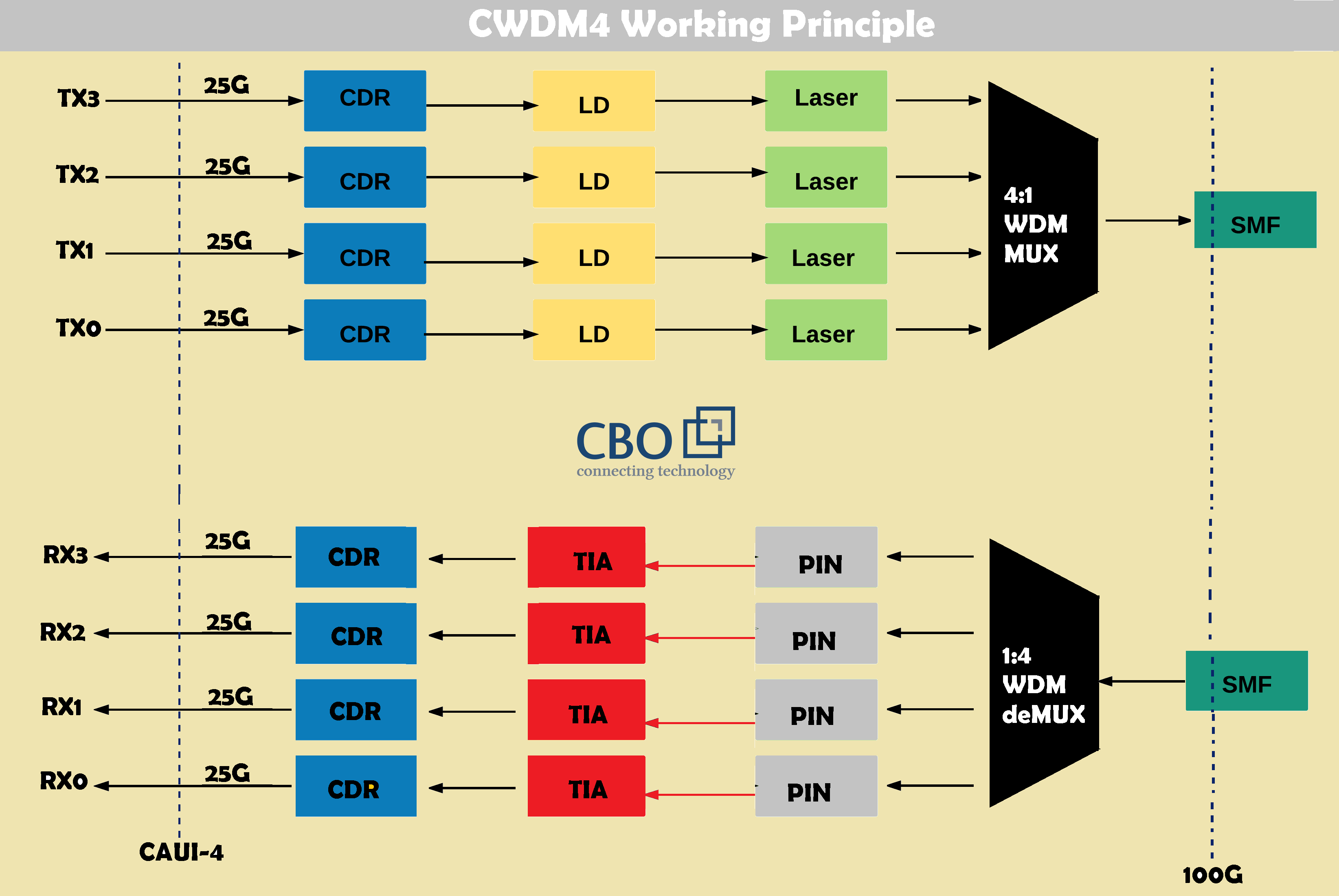
Advantages:
- Low power utilization
- Supports Digital Diagnostic Monitoring (DDM)
- High compatibility
Introduction to PSM4 Transceiver
PSM4 is specifically designed for parallel single-mode infrastructure based data centers. 100G QSFP28 PSM4 is a cost-effective solution available for optimum DCI (data center interconnect) applications up to 500 m. In this single-mode transceiver, 1310 nm wavelength is utilized for transmission, The PSM4 transmit and receive data over parallel single-mode ribbon fiber. Whereas, Standard MTP/MPO connectors are required for interfacing. This transceiver is different than CWDM4 as it uses 8 x parallel single-mode fibers (4 for transmission and 4 for receiving). With QSFP28 PSM4 100 GB/s, point-to-point links are allowed as defined by 100G PSM4 MSA (Multi-Source Agreement) standard. PSM4 operates using 4 x identical lanes per direction. Here, each lane provides a 25G optical transmission.
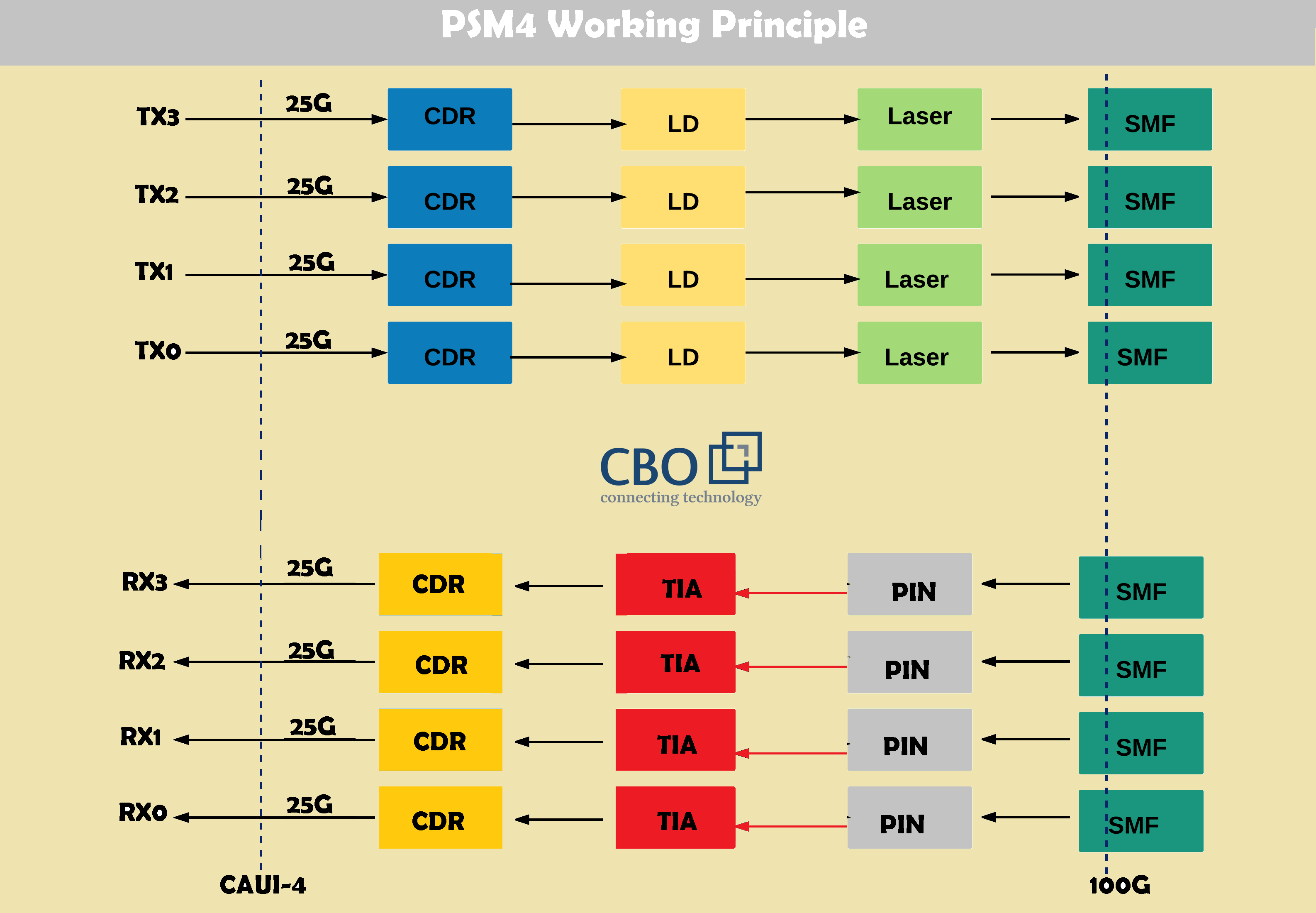
Advantages:
- Cost-effectiveness
- Simpler to deploy without optical multiplexer/de-multiplexer
- A single, uncooled DFB laser is used as a source
Similarities between CWDM4 & PSM4
Media Type: Both QSFP28 PSM4 and QSFP28 CWDM4 operate using single- mode fiber
Lane count: QFP28 PSM4 and QSFP28 CWDM4 use 4 lanes (in 4 x 25 Gbps configuration) to attain 100 Gbps
Wavelength: Wavelength of around 1310 nm is utilized in either case
Differences between CWDM4 & PSM4
Fiber count: PSM4 uses 8 single-mode fibers while CWDM4 uses 2 single- mode fibers to transmit
Transmission: Distance: In terms of transmission distance CWDM4 is superior to PSM4. (2 km and 500 m)
Connector: PSM4 interface with MTP/MPO connectors while LC duplex connectors are used with CWDM4
Cost: QSFP28 PSM4 is cheaper than QSFP28 CWDM4 (in terms of initial deployment cost only). The chart below is showing a comparison between cost factor and the distance.

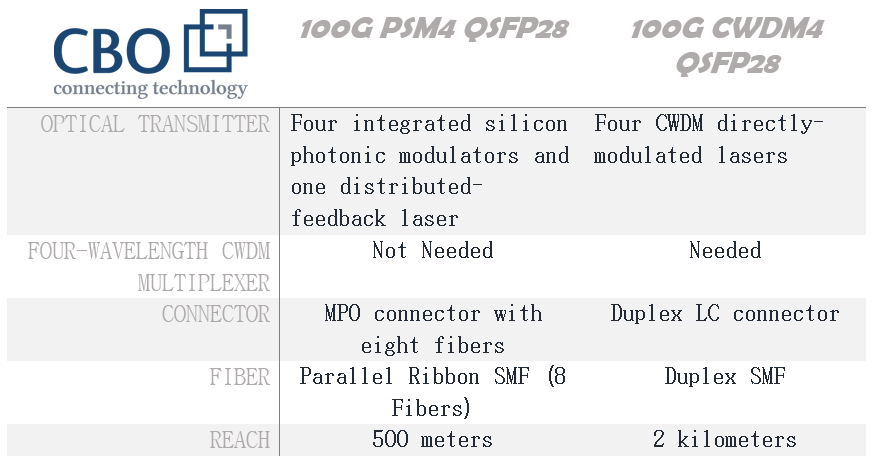
In the table below, you can find some summarized information on the similarities and differences between CWDM4 and PSM4 transceivers
Conclusion:
After looking through the facts mentioned above, we figure out that
- In various departments, PSM4 and CWDM4 are far better than other IEEE defined transceivers available on the market
- The difference between QSFP28 PSM4 and QSFP28 CWDM4 mainly lies in transmission distance, connector type, fiber count as well as cost
- PSM4 is highly recommended for transmission over single-mode fiber in short length applications
- QSFP28 CWDM4 is ideal for more extended transmission requirements (up to 2 km)
 English
English
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 Espaniol
Espaniol