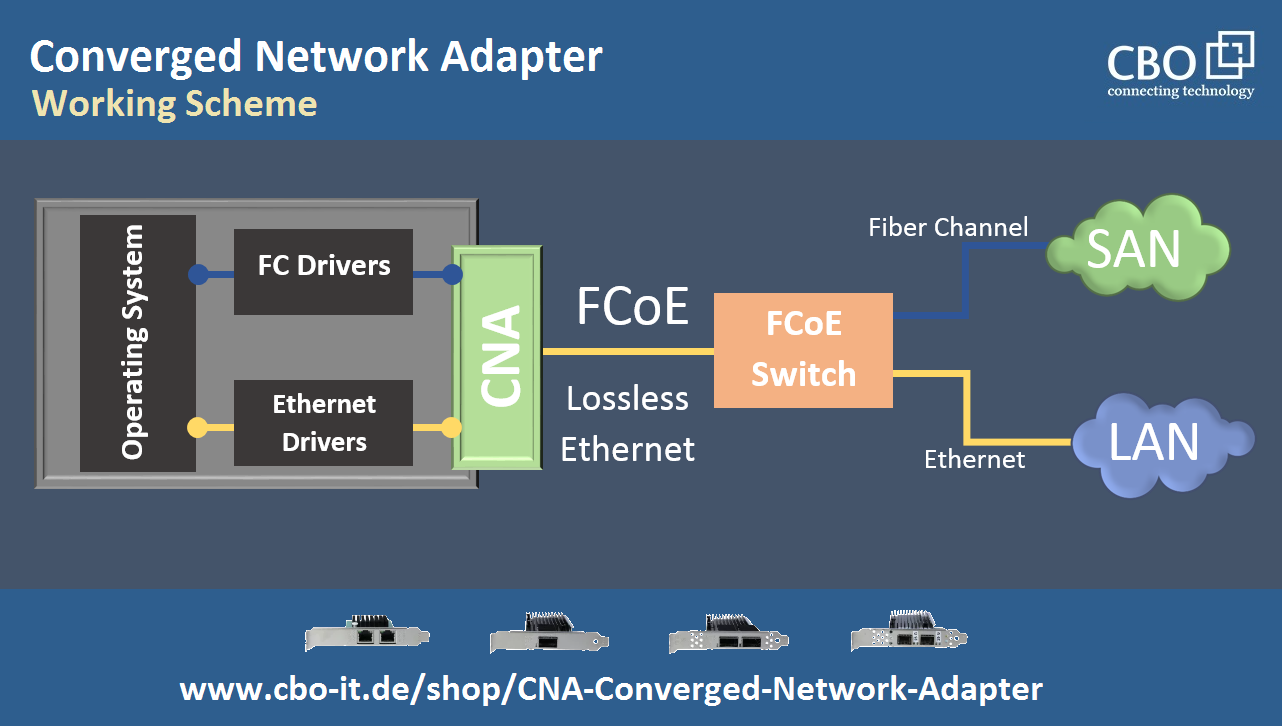
A converged network adapter (usually known as CNA) is a type of network interface card (NIC) that combines the functionality of a network interface controller and a host bus adapter (HBA) into a single card. Network adapters and HBAs have traditionally been separate entities in a computer system. Network adapters handle network communication, while HBAs connect a computer to storage devices, such as a Fiber Channel storage area network (SAN). The following block diagram informs about the concept behind the CNAs.
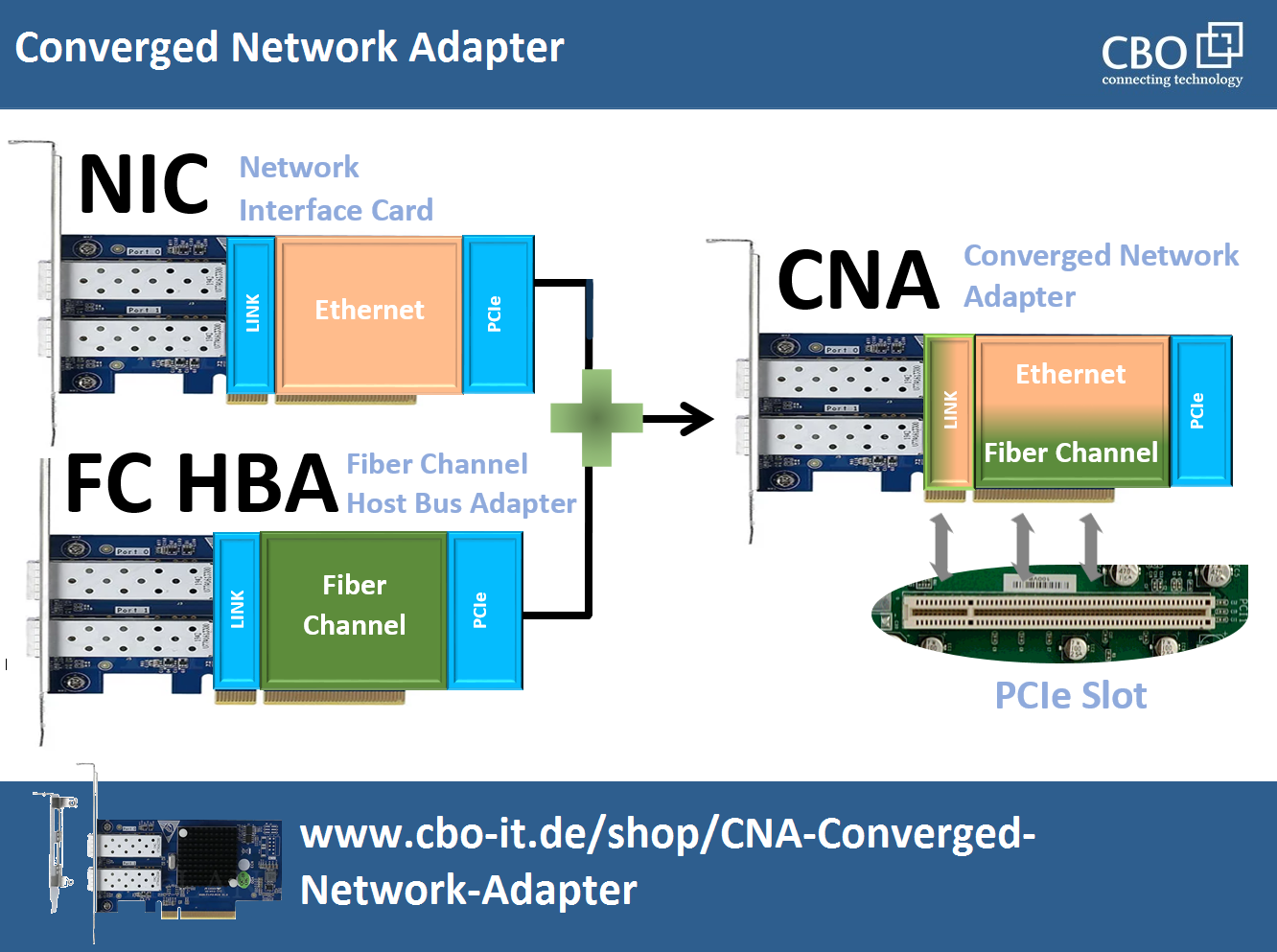
As the name suggests, a converged network adapter enables convergence by providing both network connectivity and storage connectivity over a single network interface. It supports Ethernet networking and storage protocols, such as Fiber Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) or iSCSI.
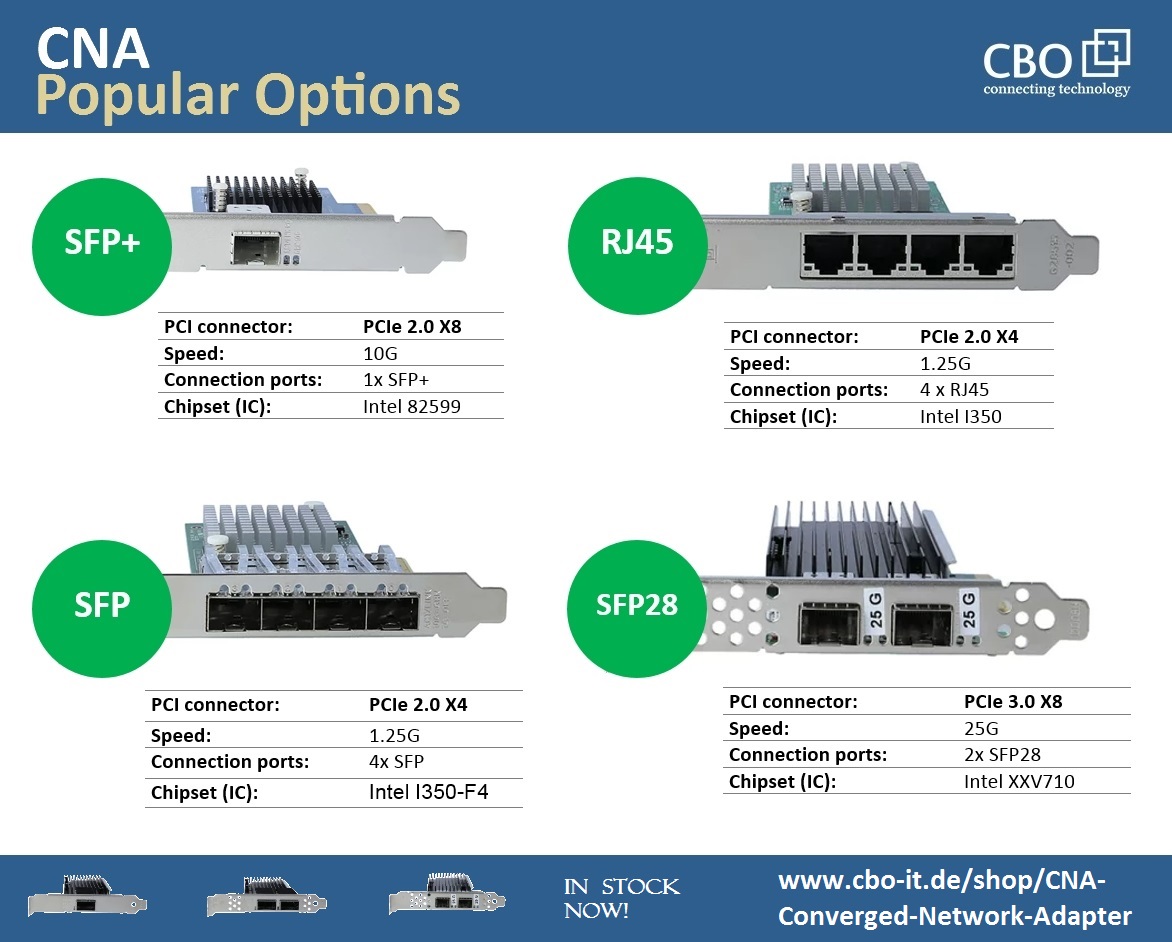
By using a CNA, organizations can simplify their network infrastructure, reduce the number of adapters needed in a system, and potentially lower costs. It allows for consolidating network and storage traffic over a unified network infrastructure, providing more flexibility and efficiency. It's worth noting that with the advancement of technology, some modern network adapters and HBAs have started integrating converged capabilities, making CNAs less common. Following are some popular CNA options available on the market.
TYPICAL APPLICATIONS OF CNAS
Converged network adapters (CNAs) are typically used in data centers and enterprise environments where there is a need to streamline network and storage connectivity. Here are a few scenarios where CNAs are commonly used:
VIRTUALIZED ENVIRONMENTS:
In virtualized environments, where multiple virtual machines (VMs) run on a single physical server, CNAs can help consolidate network and storage traffic. By utilizing FCoE or iSCSI protocols, the CNAs can connect to the VMs while enabling access to shared storage resources.
STORAGE AREA NETWORKS (SANS)
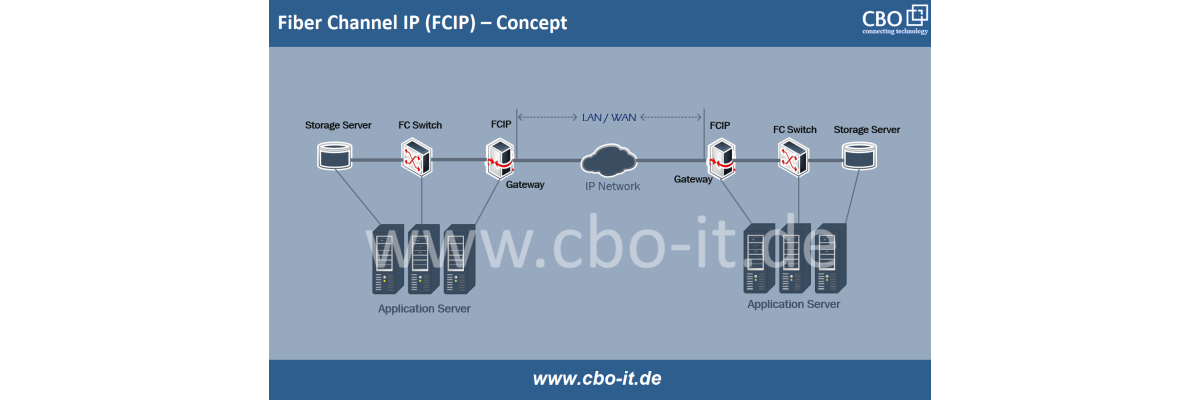
CNAs are often deployed in SAN environments requiring high-performance and low-latency storage connectivity. By supporting Fiber Channel over Ethernet (FCoE), CNAs can carry Fiber Channel traffic over Ethernet networks, eliminating the need for separate Fiber Channel HBAs. In the following exhibit, we have tried to clarify how network convergences can be obtained with the help of a CAN card.
DATA CENTER CONSOLIDATION
In situations where organizations are consolidating their data centers or reducing the number of physical servers, CNAs can help simplify the network infrastructure. By converging network and storage traffic onto a single network interface, CNAs reduce the number of adapters, cables, and switches required, leading to cost savings and improved manageability.
HIGH-PERFORMANCE COMPUTING (HPC)
CNAs can provide high-speed networking and storage capabilities in HPC environments where large-scale data processing and computational tasks are performed. This enables efficient communication between compute nodes and storage resources, enhancing overall system performance.
CLOUD COMPUTING
CNAs can be utilized in cloud computing infrastructures to optimize network and storage connectivity for virtual machines and cloud-based applications. By consolidating network and storage traffic, CNAs help improves efficiency, reduce complexity, and enhance resource utilization in cloud environments.
WHAT ARE SOME PROS AND CONS OF CNAS?
PROS:
SIMPLIFIED INFRASTRUCTURE:
CNAs allow for the convergence of network and storage traffic, reducing the number of adapters, cables, and switches required in a system. This simplifies the overall infrastructure, resulting in cost savings, easier management, and reduced complexity.
COST SAVINGS:
By consolidating network and storage connectivity onto a single adapter, CNAs can help organizations save on hardware costs. They eliminate the need for separate network adapters and Fiber Channel HBAs, reducing the number of components to purchase and maintain.
IMPROVED FLEXIBILITY:
CNAs provide flexibility by supporting multiple protocols, such as Ethernet, FCoE, and iSCSI. This allows for the consolidation of various types of traffic onto a single adapter, making it easier to adapt to changing network and storage requirements.
REDUCED POWER AND COOLING:
CNAs reduce the number of physical adapters and associated components and contribute to lower power consumption and heat generation. This can reduce energy costs and cooling requirements in data center environments.
CONS:
COMPLEXITY AND COMPATIBILITY:
Implementing CNAs can introduce additional complexity, especially in configuration, troubleshooting, and compatibility. Proper planning, configuration, and coordination with the existing network infrastructure are necessary to ensure seamless operation.
PERFORMANCE CONSIDERATIONS:
While CNAs offer convergence, there may be performance trade-offs. It's vital to consider bandwidth requirements and allocate resources appropriately. Sharing network and storage traffic on a single adapter could lead to potential congestion or increased latency if not adequately managed.
LIMITED ADOPTION:
CNAs have not been as widely adopted as initially anticipated. Advancements in networking technology, such as higher-speed Ethernet and advances in Fibre Channel, have made the need for CNAs less critical in some environments. Organizations may opt for separate adapters to maintain distinct network and storage channels.
VENDOR DEPENDENCE:
CNAs are often vendor-specific, meaning they may only work with specific server hardware and storage infrastructure from the same vendor. This can limit flexibility and increase dependency on a particular vendor's ecosystem.
While CNAs offer benefits in consolidation, cost savings, and flexibility, they also require careful consideration of performance requirements, potential complexities, and compatibility with existing infrastructure. Organizations should evaluate their needs and weigh the pros and cons before implementing CNAs.
CONVERGED NETWORK ADAPTER – FAQS
What are the benefits of using a CNA?
Using a CNA offers several benefits, including simplified infrastructure, cost savings by reducing the number of adapters, improved flexibility by supporting multiple protocols, and decreased power and cooling requirements.
What protocols does a CNA support?
A CNA typically supports Ethernet networking protocols, such as TCP/IP, and storage protocols, like Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) and iSCSI. This allows for consolidating network and storage traffic over a unified network infrastructure.
Are there any performance considerations with CNAs?
While CNAs provide convergence, there can be performance considerations. Bandwidth requirements and resource allocation should be considered to maintain optimal performance. Sharing network and storage traffic on a single adapter may lead to congestion or increased latency if not appropriately managed.
Are CNAs compatible with all server hardware and storage infrastructure?
CNAs are often vendor-specific, meaning they may be designed to work with specific server hardware and storage infrastructure from the same vendor. Verifying compatibility and ensuring proper integration with the existing network and storage environment is essential.
Can I use an RJ45 Port CAN card for running storage protocols?
No! RJ45 ports on CNAs are typically associated with Ethernet connectivity rather than storage protocols like Fiber Channels. If you require Fiber Channel connectivity, a CNA with Fiber Channel ports or Fiber Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) support would be more appropriate.
How many ports can there be on a CNA card?
It's important to note that the specific number of ports and the types of ports (Ethernet, Fiber Channel, or iSCSI) on a CNA card can vary depending on the manufacturer, model, and specific card requirements. It is advisable to refer to the documentation or specifications of a particular CNA card to determine its specific port and interface configuration.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, converged network adapters (CNAs) can consolidate network and storage connectivity onto a single card, providing several benefits in data centers and enterprise environments. CNAs simplify infrastructure by reducing the required adapters and cables, resulting in cost savings and easier management. They support multiple protocols, such as Ethernet, Fiber Channel over Ethernet (FCoE), and iSCSI, enabling network and storage traffic convergence.
While CNAs offer advantages like flexibility and reduced power consumption, there are considerations such as potential performance trade-offs and compatibility with existing infrastructure. CNAs provide a means to streamline network and storage connectivity, but their implementation should be carefully planned and evaluated based on specific requirements and the existing technology ecosystem.
 English
English
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 Espaniol
Espaniol