Bidirectional (BiDi) transmission refers to the ability to send and receive data over a single fiber optic cable in both directions simultaneously. This technique is especially valuable in fiber optic communications, as it effectively doubles the capacity of existing fiber infrastructure without the need for additional cables.

BiDi transmission is achieved through the use of specialized optical components that can separate the light signals traveling in opposite directions. Here's how it works in more detail:
How BiDi Transmission Works?
Transmission:
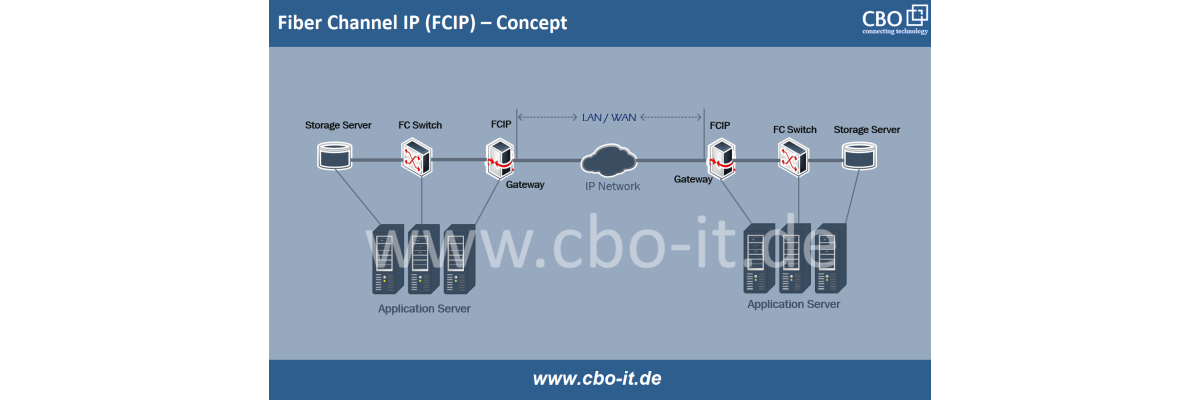
Data is converted into light signals using a laser or LED. In a BiDi system, each end of the fiber link uses a different wavelength for transmission. This allows the signals to be distinguished from each other when they travel back and forth on the same fiber. The following exhibit shows how BiDi transmission is different;
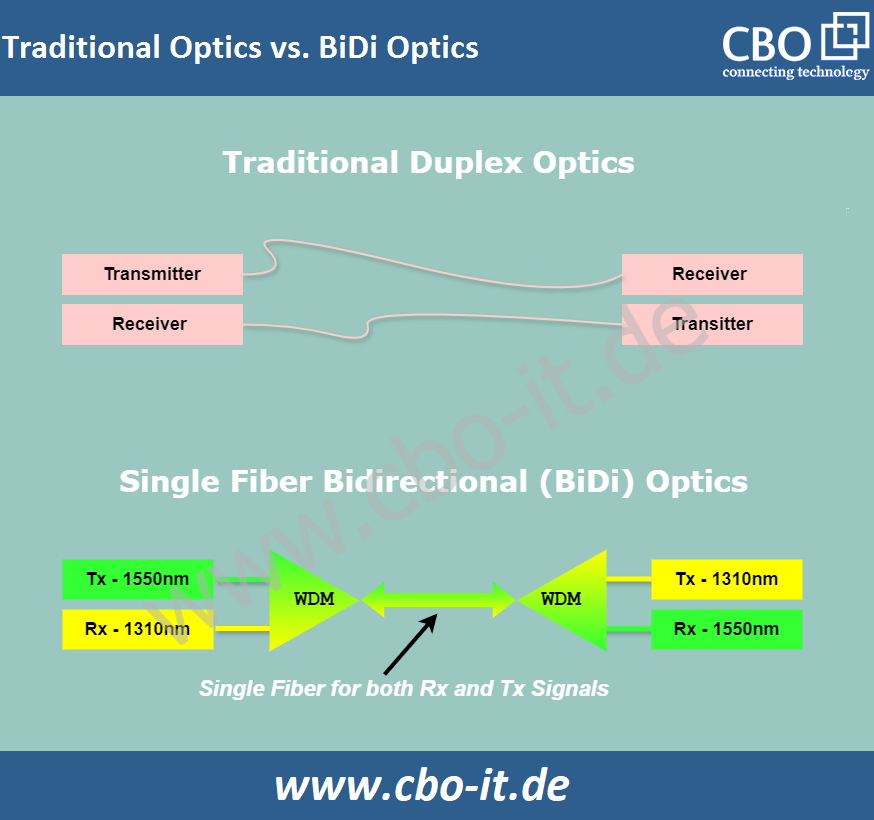
Propagation:
The light signals propagate through the fiber optic cable, carrying data to their destination. Despite traveling in the same physical medium, the signals at different wavelengths do not interfere with each other significantly.
Reception:
At the receiving end, optical filters or WDM devices separate the incoming light based on its wavelength. The receiver then converts the light signal back into data. Each end of the link receives the wavelength that its transceiver is designed to detect, ensuring that the correct data is received.
Key Components of BiDi Transmission Systems
Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) Devices:
BiDi transmission often relies on WDM technology, specifically utilizing two different wavelengths of light for the two directions of communication. For example, one wavelength (e.g., 1310 nm) might be used for sending data, while another wavelength (e.g., 1550 nm) is used for receiving data on the same fiber.
BiDi Transceivers:
These are specialized transceivers designed to support bidirectional communication over a single fiber. Each transceiver is capable of transmitting data at one wavelength and receiving data at another wavelength. BiDi transceivers are paired so that each end of the fiber link transmits and receives on complementary wavelengths.
Mature BiDi Technologies
Mature BiDi technologies are integrated into various networking equipment, offering solutions across a range of data rates to accommodate different network scales and applications. Here's an overview of some common BiDi options available:
1G BiDi:
Typically used for short to medium-distance communications within a local area network (LAN) or on campus networks. These are often implemented in small business or enterprise networks for efficient data transmission.
10G BiDi:
Offers higher data rates suitable for data centers, enterprise networks, and service provider backhauls. The 10G BiDi solutions can support longer distances than 1G, making them suitable for metropolitan area networks (MANs) or even some longer-haul connections.
25G, 40G, and 100G BiDi:
These are advanced options that provide significantly higher bandwidth and are designed to meet the demands of modern data centers, large enterprises, and high-speed network backbones. They are especially beneficial in scenarios where high data throughput and bandwidth efficiency are critical.
BiDi Technology Advantages
- Cost Efficiency: BiDi technology reduces the need for additional fiber cables, which can be costly and complex to install, especially in densely populated or difficult-to-access areas.
- Increased Capacity: By enabling simultaneous two-way communication on a single fiber, BiDi effectively doubles the network capacity without additional physical infrastructure.
- Simplicity and Scalability: Deploying BiDi modules simplifies network architecture and makes it easier to scale the network up or down based on demand.
BiDi Technology Disadvantages
- BiDi systems rely on precise wavelength division to separate the send and receive signals. This necessitates precise and stable wavelength-specific lasers and filters, which can be more sensitive to temperature fluctuations and may require more sophisticated temperature control mechanisms.
- There's a potential risk of optical interference between the upstream and downstream signals if the wavelengths are not properly isolated, which can degrade signal quality.
- Upgrading BiDi systems can be more complex than traditional ones, as new components must be carefully selected to ensure compatibility with existing BiDi wavelengths and equipment.
- Diagnosing and resolving issues in a BiDi system can be more complex due to the simultaneous transmission of signals in both directions on a single fiber.
- BiDi optics can be more expensive than traditional unidirectional optics due to their complexity and the need for precise wavelength control.
BiDi Technology – Common Applications
BiDi transmission is used in various applications, including but not limited to:
- Fiber to the Home (FTTH) networks, where it maximizes the efficiency of fiber deployment to individual residences.
- Data center interconnects, where space and fiber resources are at a premium.
- Metropolitan area networks (MANs) and wide area networks (WANs), where it can significantly increase the capacity of existing fiber infrastructure.
Considerations for BiDi Implementation
- Wavelengths: BiDi transmission uses two different wavelengths, typically one for upstream and one for downstream communication. It's important to ensure that the equipment on both ends of the fiber supports the correct wavelengths for proper operation.
- Compatibility: Network devices (such as switches and routers) must be compatible with BiDi transceivers. It's crucial to verify that the equipment supports the specific BiDi standards and speeds required for your network.
- Distance and Budget: The distance over which the data needs to be transmitted and the available budget are key considerations. Higher-speed BiDi solutions (like 40G and 100G) can be more expensive but are necessary for long-distance and high-capacity requirements.
Conclusion
In conclusion, BiDi technology offers a flexible and cost-effective way to enhance the capacity of fiber optic networks. With options ranging from 1G to 100G, there are BiDi solutions available for a wide range of network scenarios, from small enterprise setups to large-scale data centers and metropolitan area networks.
 English
English
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 Espaniol
Espaniol