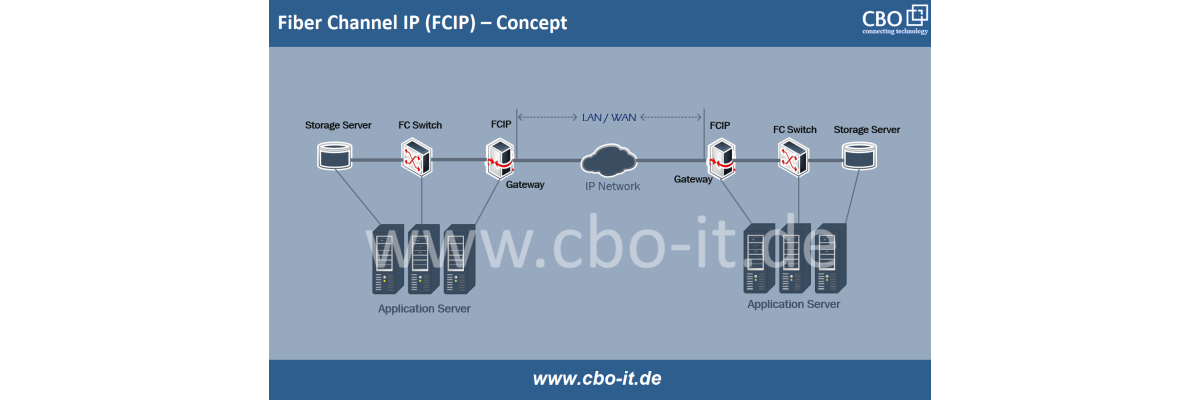
Network engineers face several complex decisions when selecting the most appropriate fiber optic cabling for their individual and specific requirements. Should it be a multimode or a singlemode fiber? In the case of multimode, a graded index or step index fiber? These are just two of the many questions that need to be addressed when selecting a fiber optic solution.
In many cases, the best tactic is to identify and understand the specific application for which the fiber optic cable is needed, and then evaluate many options to end up with the type of fiber optic cable that is best suited. How important are latency, bandwidth, speed, etc.? What is the required link distance? Are there budget constraints? Knowing the answers to these questions can help in the decision-making process.
STEP INDEX Vs. GRADED INDEX
Both step index and gradient index are two types of multimode fibers. In step index fibers, the refractive index of the core remains the same. Therefore, light rays traversing a step index fiber travel at the same speed, and rays traveling a shorter path arrive earlier than rays traveling a longer path.
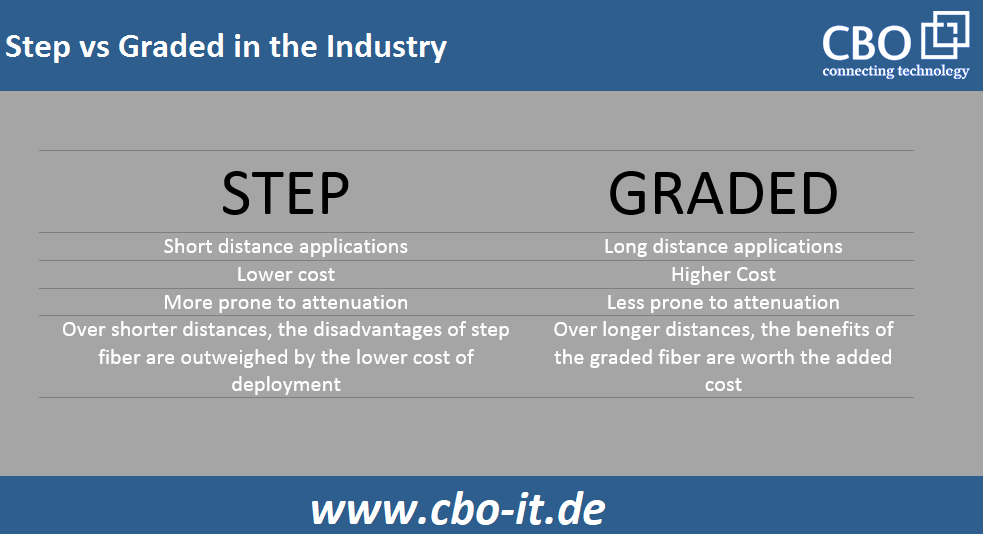
In graded refractive index fibers, the maximum refractive index is in the central region, limiting the speed of rays moving through the center. On the other hand, the refractive index of the core of a graded fiber decreases toward the cladding. Therefore, the different rays of light traveling through a graded-index fiber move at different speeds. In contrast, the rays passing through the edge regions of the core travel at higher speeds. As a result, all light rays passing through a graded index fiber take almost the same time to exit.
When should GRADED INDEX FIBER be used?
.png)
A graded index fiber is an optical fiber whose refractive index in the core is inversely proportional to the radial distance. In other words, the refractive index of the core decreases with increasing radial distance. According to ITU standards, the graded index fiber is classified as G.651.1.
Gradient index fibers are considered the optimal solution in many applications. Like many other multimode fibers, graded index fiber is often considered most suitable and practical for short-haul applications. In comparison, graded index fiber offers lower modal dispersion than step index multimode fiber, which is why it can handle comparatively higher transmission bandwidths.
GRADED INDEX FIBER for REDUCED MODAL DISPERSION
Modal dispersion occurs when multiple modes or waves of light travel different paths within a single fiber. When the light travels different paths, some signals carry and reach the receiver earlier than others. This results in a lower bandwidth and a broadening of the signal. Mode dispersion limits the bandwidth of the signal to a few tens of MHz per kilometer, i.e., for a 1-kilometer link, the bandwidth of the signal cannot exceed a few tenths of MHz.
As mentioned above, multimode fibers can have either a step index or a graded index. Graded index offers numerous advantages over step index multimode fibers and significantly reduces modal dispersion. Modal dispersion can be further reduced using smaller core size fibers, such as 50um, found in OM3 and OM4 fiber optic cables available today, allowing transmission rates up to 10G and even beyond several hundred meters.
GRADIENT INDEX FIBER - ADVANTAGES
• Light beams move in a controlled manner
• It is ideal for long distance applications
• It is less susceptible to damping
• All rays crossing the core of a gradient fiber take almost the same time to arrive at the receiver
GRADIENT INDEX FIBER - IDEAL APPLICATIONS
With their ability to deliver high bandwidth over short and medium distances, graded index fibers are the ideal choice for a variety of applications such as;
Commercial and Residential: Gradient index fiber can be a viable networking solution for commercial and residential buildings, including but not limited to homes, offices and buildings.
Data centers: Today's data centers are under immense pressure to provide high bandwidth applications over singlemode fiber. However, graded index multimode fiber, especially OM4 and OM3, can also be used in data centers due to its high bandwidth.
Large ships: Communication networks have become important everywhere, including the high seas. The tiered fiber index with high bandwidth is an excellent choice for large ships.
Small campuses and local area networks: campuses and buildings have local area networks; graded index fiber can provide better distance and bandwidth, especially between and across different facilities on campus.
Conclusion:
The main advantage of graded index fiber over the other types is its tendency to minimize model dispersion. Graded index fibers are more expensive than step index fibers, but the higher cost is offset by higher bandwidths and longer link distances. However, you can determine the most appropriate fiber type after analyzing the bandwidth and speed requirements of your specific applications and other factors.
 English
English
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 Espaniol
Espaniol