What are multiplexing Technologies?
In optical fiber communication, multiplexing is a key technique used to enhance the capacity of existing fiber network infrastructure. It enables multiple separate signals to be sent over the same communication channel, leading to better utilization of the channel. With multiplexing, several signals can coexist in the same transmission medium by leveraging different parameters or dimensions. This allows the signals to be transmitted simultaneously without interfering with each other. The main multiplexing technologies in use today are wavelength division multiplexing (WDM), time division multiplexing (TDM), frequency division multiplexing (FDM), and code division multiplexing (CDM). These technologies will be further explored in detail.
Wavelength Division Multiplexing
Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) is a technique used in optical networking to increase bandwidth by combining multiple optical carrier signals onto a single fiber using different wavelengths. Each signal at a specific wavelength is independent of any protocol or speed, allowing for bidirectional communication over a single fiber. This simplifies the network by creating a virtual optical fiber network, reducing the need for multiple fibers and lowering networking costs.
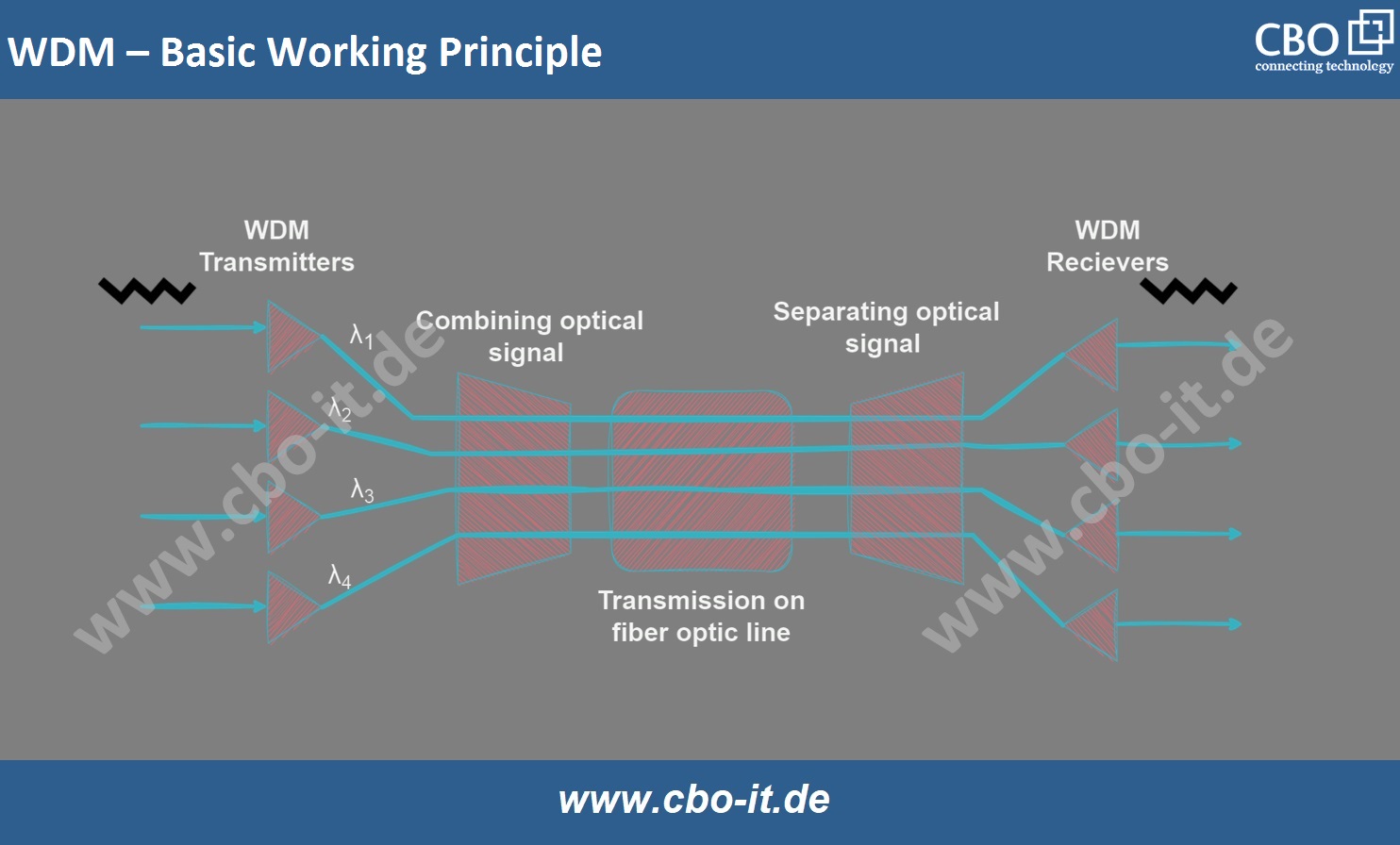
There are two types of WDM systems: Coarse Wave Division Multiplexing (CWDM) and Dense Wave Division Multiplexing (DWDM). Both CWDM and DWDM use multiple wavelengths on a single fiber, but they differ in the spacing of the wavelengths, number of channels, and the ability to amplify signals. In a WDM system, optical signals are combined at one end of the fiber and separated into different channels at the other end.
Time Division Multiplexing
Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) is a method that involves splitting various signals into time slots and then transmitting them in the sequence of these slots. In the realm of optical communication, Optical Time-Division Multiplexing (OTDM) is a specific form of TDM that leverages the time precision of optical pulses to multiplex optical signals.
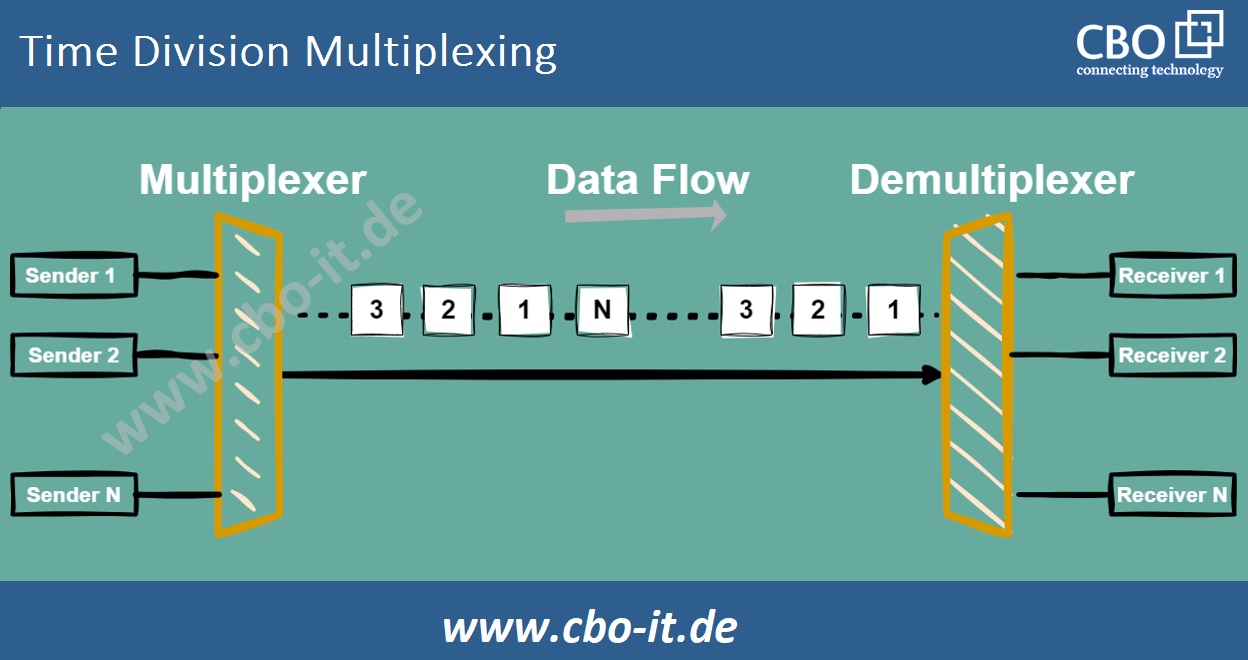
OTDM essentially combines multiple low-bit-rate optical channels within a set electrical clock period, thereby enhancing transmission speed. Each signal is sent by segmenting the time frame into time slots, with each slot designated for a message signal. By assigning each low-speed channel to a specific position based on time, the system operates in synchronization. Consequently, OTDM achieves multiplexing of multiple signals by temporally segmenting and interleaving various optical channels.
Typically, the optical pulse width is reduced to accommodate more channels within the fixed clock period. This reduction in pulse width can also minimize crosstalk between channels due to the increased bit rate capacity. However, a shorter pulse width can lead to significant dispersion as the signal travels over longer distances. To counter this dispersion effect in OTDM, techniques such as using transform-limited pulses and dispersion slope compensation are employed to mitigate dispersion issues and optimize signal quality.
Space Division Multiplexing (SDM)
Space Division Multiplexing (SDM) is a technology that leverages spatial dimensions to transmit multiple data streams simultaneously through parallel spatial channels. This method is commonly employed in systems like Multi-Input Multi-Output (MIMO), which uses multiple antennas at both the transmitting and receiving ends. MIMO signal processing is already extensively used in coherent optical transmission systems, particularly with Polarization Division Multiplexing (PDM) over standard single-mode fibers.
By implementing strategies that involve multi-core and multi-mode fibers, it is believed that SDM can enable long-distance transmission and high-speed data rates. The advent of SDM technology presents a new avenue for enhancing the capacity of optical cable transmission systems. Researchers are exploring the integration of SDM in submarine optical cables to boost transmission capacity in recent years.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this article has discussed three main multiplexing technologies used in optical communication: Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM), Time Division Multiplexing (TDM), and Space Division Multiplexing (SDM). These technologies are essential for enabling efficient data transmission. Following quick comparison can help you understand the difference between various multiplexing technologies!
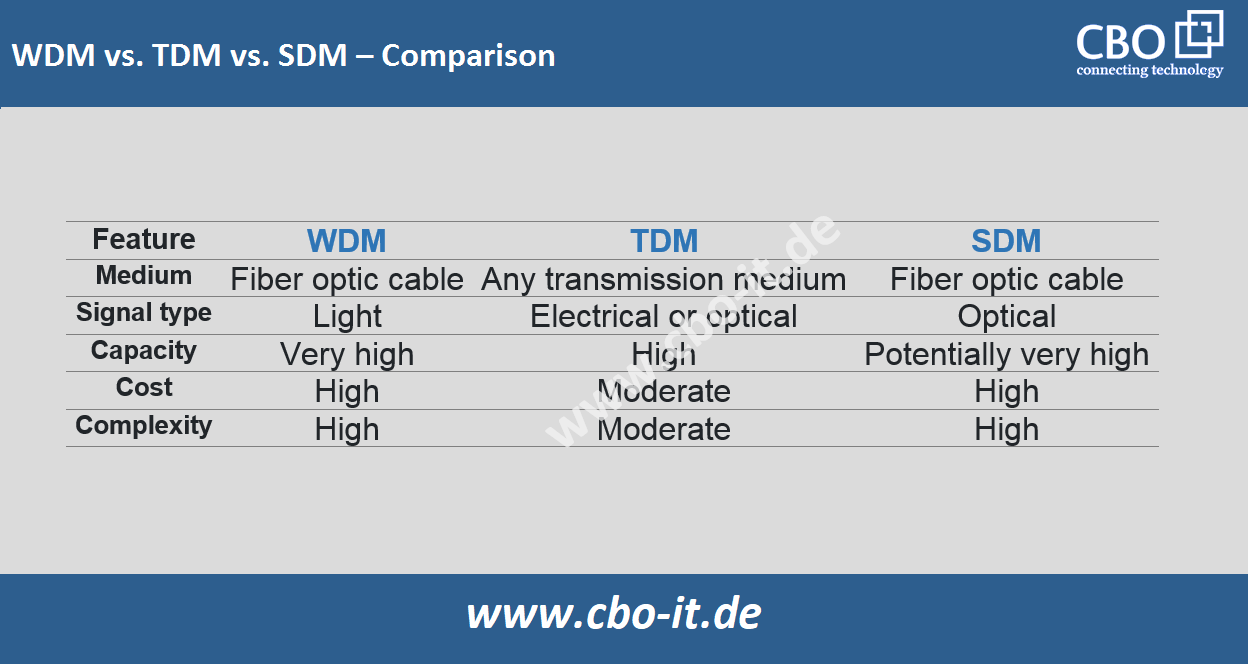
Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) is the most widely used multiplexing technology in optical communication. Each of these techniques has its own strengths and limitations, so it is often recommended to combine multiple techniques in fiber optic networks to achieve optimal transmission performance.
 English
English
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 Espaniol
Espaniol