A data center is a centralized facility used for storing, processing, managing, and disseminating data and information. It typically houses many computer systems, servers, networking equipment, and storage systems, all interconnected to support the computing and data storage needs of organizations.
Key features of a data center include:
Servers and Hardware:
Data centers house many servers, which are powerful computers designed to handle various tasks such as processing data, running applications, and managing network resources.
Networking Infrastructure:
Data centers have robust networking infrastructure to facilitate communication between servers and to connect the data center to the broader network, including the Internet.
Storage Systems:
Data centers include storage solutions like hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SSDs) to store and retrieve data. Storage systems are crucial for maintaining large volumes of information.
Cooling and Power Systems:
Data centers generate significant heat due to the continuous operation of servers and other equipment. Therefore, they have cooling systems in place to maintain optimal temperatures. Additionally, data centers require reliable power sources and backup systems to ensure uninterrupted operation.
Security Measures:
Given the sensitive nature of the data stored in data centers, security is a top priority. Data centers employ physical security measures, such as access controls and surveillance, as well as cybersecurity measures to protect against unauthorized access and cyber threats.
Redundancy and Reliability:
To ensure continuous operation, data centers often incorporate redundancy in critical components, such as power supplies, networking, and storage. This helps prevent downtime in the event of equipment failure.
Scalability:
Data centers are designed to be scalable, allowing organizations to expand their computing and storage resources as their needs grow.
Remote Management:
Many modern data centers allow for remote management, enabling administrators to monitor and control the infrastructure from a distance.
What are some types of Data Centers?
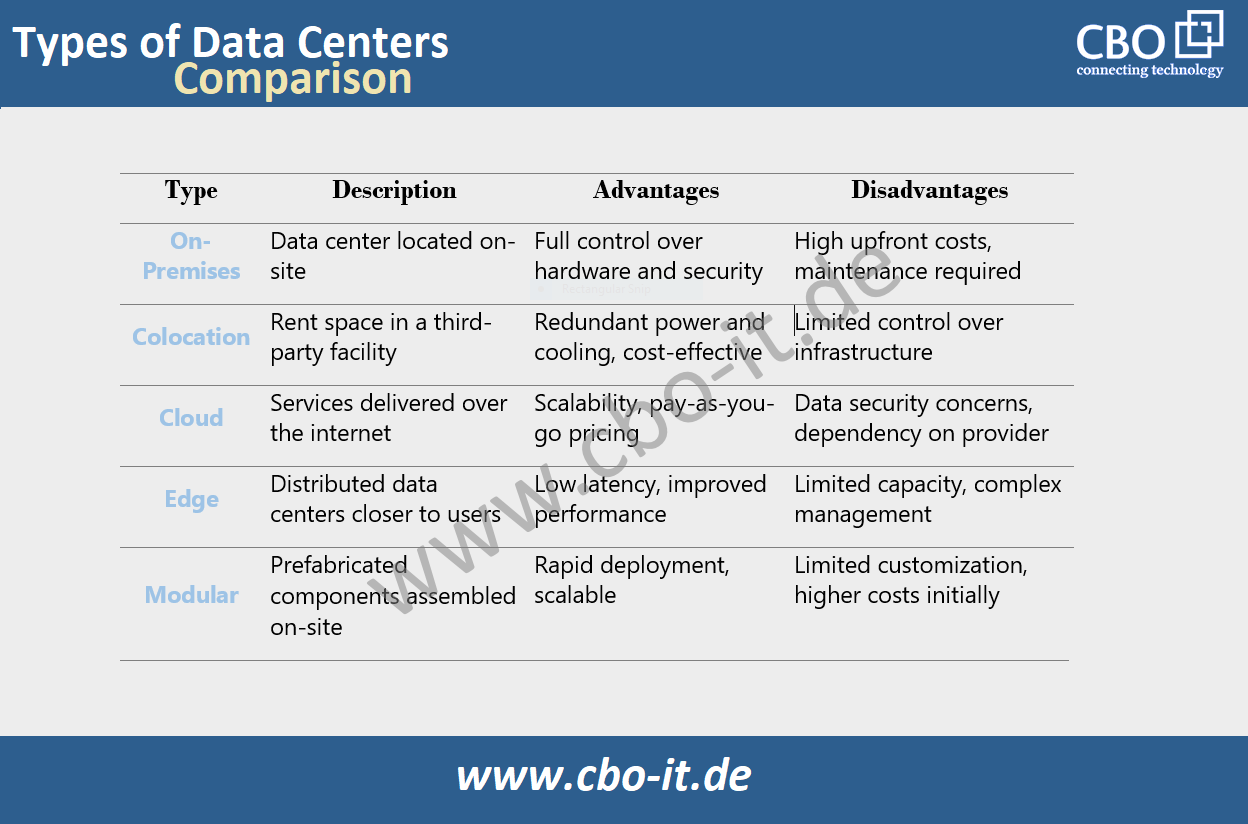
Below are some prominent types of data centers, each catering to distinct needs within the dynamic landscape of information technology.
Enterprise Data Centers
Owned and operated by individual enterprises or organizations to meet their specific IT needs. These data centers support a single business entity's computing and data storage requirements. Examples include data centers run by corporations, government agencies, and educational institutions.
Internet Data Centers (IDCs)
Facilities provide hosting services to various customers, typically on a subscription basis. IDCs offer businesses and individuals web hosting, email hosting, and other cloud-based services. Examples include major cloud service providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
Colocation Data Centers
Facilities where multiple organizations or tenants rent space for their servers and IT infrastructure. In colocation data centers, tenants bring their servers and equipment, while the facility provides essential services such as power, cooling, physical security, and networking infrastructure. Examples of colocation data center providers include Equinix and Digital Realty.
Cloud Data Centers
Represent infrastructure cloud service providers use to deliver scalable computing and storage services over the Internet. Cloud data centers enable users to access and scale computing resources without needing on-premises hardware. Major players in this space include AWS, Azure, GCP, and other cloud service providers.
Regional Data Centers
Facilities designed to serve a specific geographic region or locality. These data centers cater to the IT needs of businesses and organizations within a particular area, addressing regional data processing requirements. Examples may include data centers serving specific regions or cities.
Edge Data Centers
Facilities located closer to end-users or devices to reduce latency and improve performance for applications that require real-time processing. Edge data centers support edge computing, facilitating faster data processing for applications like the Internet of Things (IoT), content delivery, and critical services. Examples include EdgePoint and Vapor IO.
Modular/Containerized Data Centers
Data centers are built using modular components or containers, allowing rapid deployment and scalability. These data centers offer flexibility in expanding capacity quickly and efficiently. Examples of modular/containerized data centers include solutions provided by companies like Schneider Electric and Dell.
A Brief Description of Data Center Operation
A data center is a centralized facility for processing, storing, managing, and disseminating data and information. Here's a general overview of how a data center operates:
Data Processing
Data centers process vast amounts of information using servers and computing equipment. These servers handle various tasks, such as running applications, performing calculations, and managing databases.
Storage
Data centers store large volumes of data on storage systems, including hard disk drives (HDDs), solid-state drives (SSDs), or other storage technologies. This stored data can include files, databases, and other digital assets.
Networking
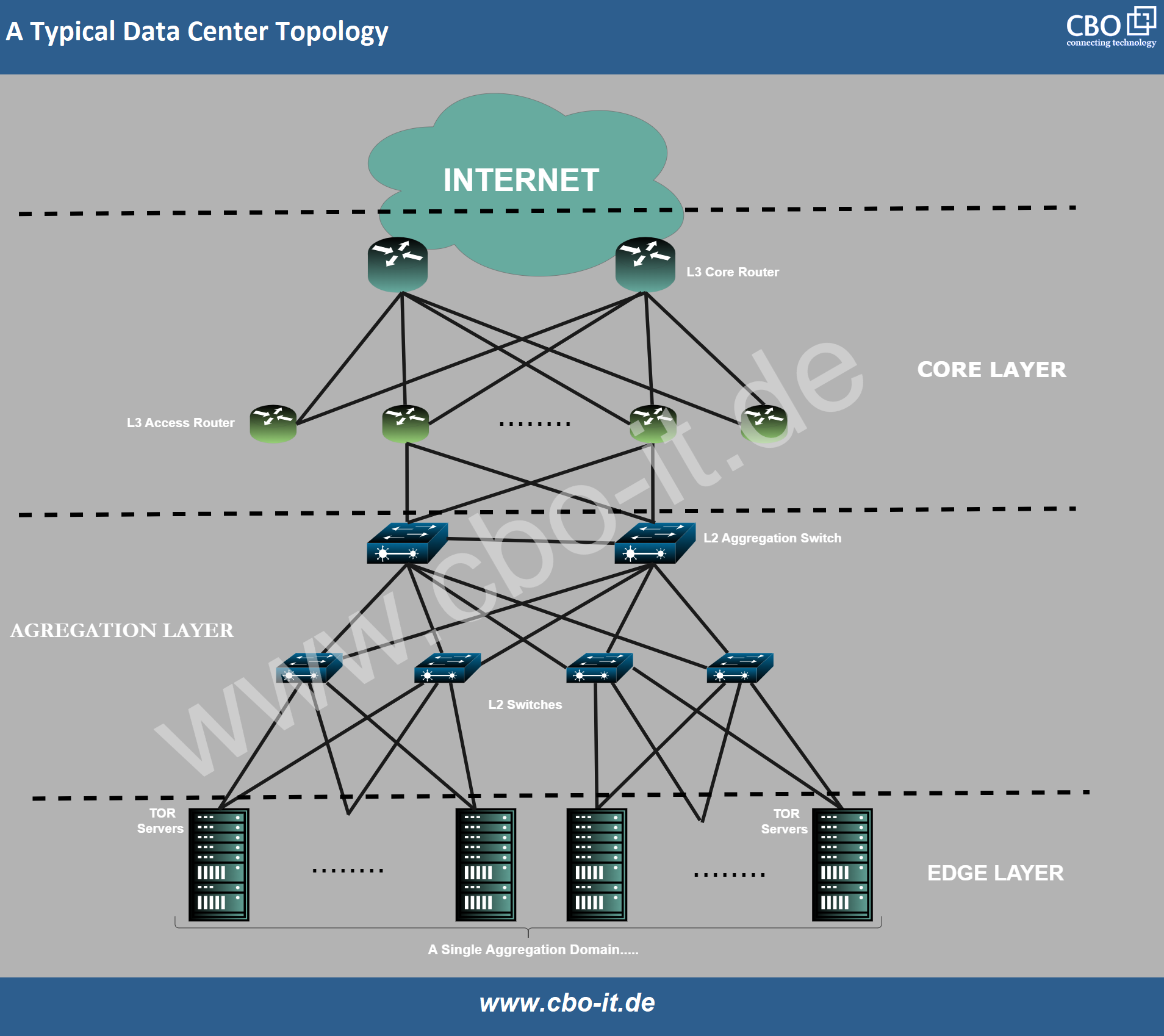
Robust networking infrastructure connects servers within the data center and links the data center to external networks, including the Internet. This enables server data transfer and facilitates communication with other devices and services.
Conclusion
In conclusion, data centers are critical facilities that support the computing and data storage needs of organizations. They are designed to be scalable, secure, and reliable, with features like servers and hardware, networking infrastructure, storage systems, cooling and power systems, security measures, redundancy and reliability, scalability, and remote management. There are different types of data centers, each catering to distinct needs, including enterprise, internet, colocation, cloud, regional, edge, and modular/containerized data centers. With the increasing importance of data and information, data centers are becoming more crucial than ever, and they continue to evolve to meet the dynamic and diverse needs of organizations.
 English
English
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 Espaniol
Espaniol