Passive optical network (PON) technology was introduced in the mid-1990s. After that, PON technology underwent rapid development - it started with ATM PON (APON) and then evolved into Broadband PON (or BPON). Later, EPON (Ethernet PON) and GPON (Gigabit PON) entered the market, bringing significant improvements in transmission bandwidth and distance. In this paper, we will discuss the basics of GPON technology.
Basic components of the GPON network
ITU-T G.984 forms the basis for Gigabit Passive Optical Networking (GPON). GPON offers more bandwidth than BPON and APON and is suitable for various applications. The four essential GPON components are listed below;
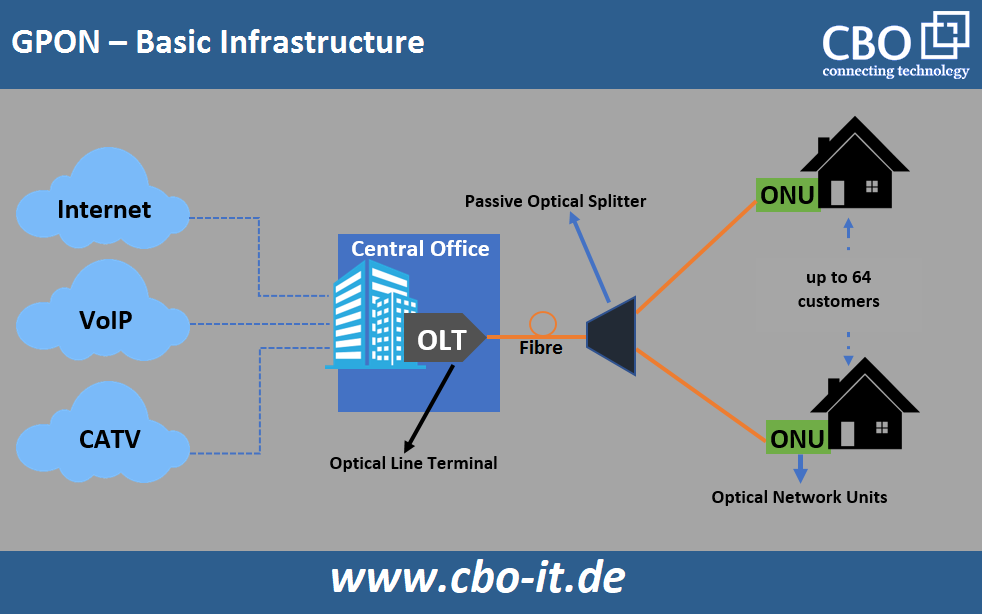
Optical Line Terminal (OLT)
An Optical Line Terminal is an active Ethernet aggregation or accumulation device. It also plays the role of network manager by regulating all traffic on the GPON network in the form of voice, data and video signals. Generally located in the data center or main equipment room, OLTs receive electrical signals and send these signals to the associated ONTs in the form of optical signals via optical splitters. It also converts the aggregated optical signals from the end-user ONTs into electrical signals and forwards them to one or more Core Ethernet switches.
The signals that an OLT receives from the end users are called upstream signals. The signals it sends to the end users are called downstream signals. We use different light wavelengths for upstream and downstream signals to avoid interference between the two signals. For upstream traffic we use 1310nm, for downstream traffic 1490nm (for voice and data) and 1550nm (for video).
Transport media - cabling
GPON networks use passive, physical cabling infrastructure for signal transmission. Transmission media includes adapter plates, splitters, connectors, fiber patch cables, copper patch cables, enclosures, horizontal and backbone cable covers, and support material for routing. All cabling components must be included in the link or channel loss budget when validating system performance.
Passive optical splitter
Passive optical splitters belong to the group of transporting media components. These splitters enable communication with multiple devices over a single incoming fiber optic cable. Passive optical splitters use multiple silica waveguides to split a single strand into two strands. The number of outputs on a passive optical splitter is equal to the number of splits. Each splitter causes a signal loss of about -3 dB.
Optical Network Terminal (ONT)
The ONT (Optical Network Terminal) serves as a modem in a GPON network. ONTs convert optical signals from OLTs into electrical signals, which are then forwarded to the user's terminal equipment. An ONT is connected to the termination point at the user's site via a fiber optic cable and connected to the modem via an Ethernet cable. Most ONTs are equipped with redundant Ethernet ports.
.png)
GPON loss budget
A PON network typically includes ONUs, OLTs and other optical transmission hardware such as splitters, connectors and cables. Each component involved in a GPON network introduces some signal loss. Estimating the link loss budget and optimizing it is critical and must be done during the design phase - well before actual deployment. The following table shows the allowable channel attenuations for various GPON applications.
.png)
GPON Performance Budget
The sensitivity of the receiver and the power of the transmitter are two main parameters that determine the maximum range of the access network. The formula for calculating the power budget is;
P= FCA x L + SL +Penalties
Wo:
P stands for the power budget
FCA stands for the attenuation of the fiber optic cable (in dB/m)
L stands for the connection distance
SL represents the distribution losses (total distribution losses)
Penalties stand for additional losses (due to connectors, splices, etc.)
The following chart shows the minimum power budget for different GPON configurations;
.png)
Conclusion:
GPON is the most improved version among the different PON types. With GPON, commercial network operators can achieve great benefits. In this article, we have discussed the main GPON components and their functions. We also briefly discussed the concept of link loss and optical power budgets. It is important to understand that you should not start physically setting up a link until you have made thorough estimates of link performance and loss budget.
 English
English
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 Espaniol
Espaniol