We are living in an Internet-driven world. Today`s Internet connectivity is much better than what we had a couple of decades ago. Let it be banking, shopping, entertainment, education, gaming, or anything else – the Internet has a role to play. Today, service providers are looking for better and economical ways to provide their subscribers with excellent and reliable services.
The concept of triple-play service also demands a robust and reliable networking mechanism. Here, it is important to understand that the Internet is a complex arrangement of hardware and software resources and it has several layers. The topic of this article is related to the distribution layer and more specifically about the last mile.
Last-mile networking has always remained the most challenging area for network operators. In most parts of the world, already laid copper-based networks were utilized for the delivery of the internet. But copper is not that ideal medium as it can’t withstand the bandwidth nor speed requirements of modern, Internet-based services. So, service providers came ahead with an idea of FTTX or fiber-to-the-x. In various FTTX configurations, fiber replaces copper at the distribution layer and in some cases at the network access layer as well.
What is Fiber to the X or FTTx?
Fiber to the X or FFTX is a generic term which is used for referring to various fiber deployment configurations FTTx or fiber-to-the-x is used to describe network architectures in which optical fiber cables are utilized for all or part of last-mile telecommunications. Optical fiber cables offer numerous advantages over copper cables especially in medium to long-distance applications. FTTx can be classified into two groups;
- Architectures in which fiber is laid to the home, building or premises
- Architectures in which fiber is laid to the node/cabinet
Benefits of the FTTX
Undoubtedly, FTTX is the optimal solution available for dealing with the upcoming demand of bandwidth and speed and there are several benefits of replacing the already existing, less-efficient last-mile communication channels with optical fiber. In the following exhibit, we have tried to explain how an internet business transformed its services by upgrading the existing system and incorporating FTTH.
Following are some of the most obvious benefits of using optical fiber cable for delivering broadband services to the subscriber;
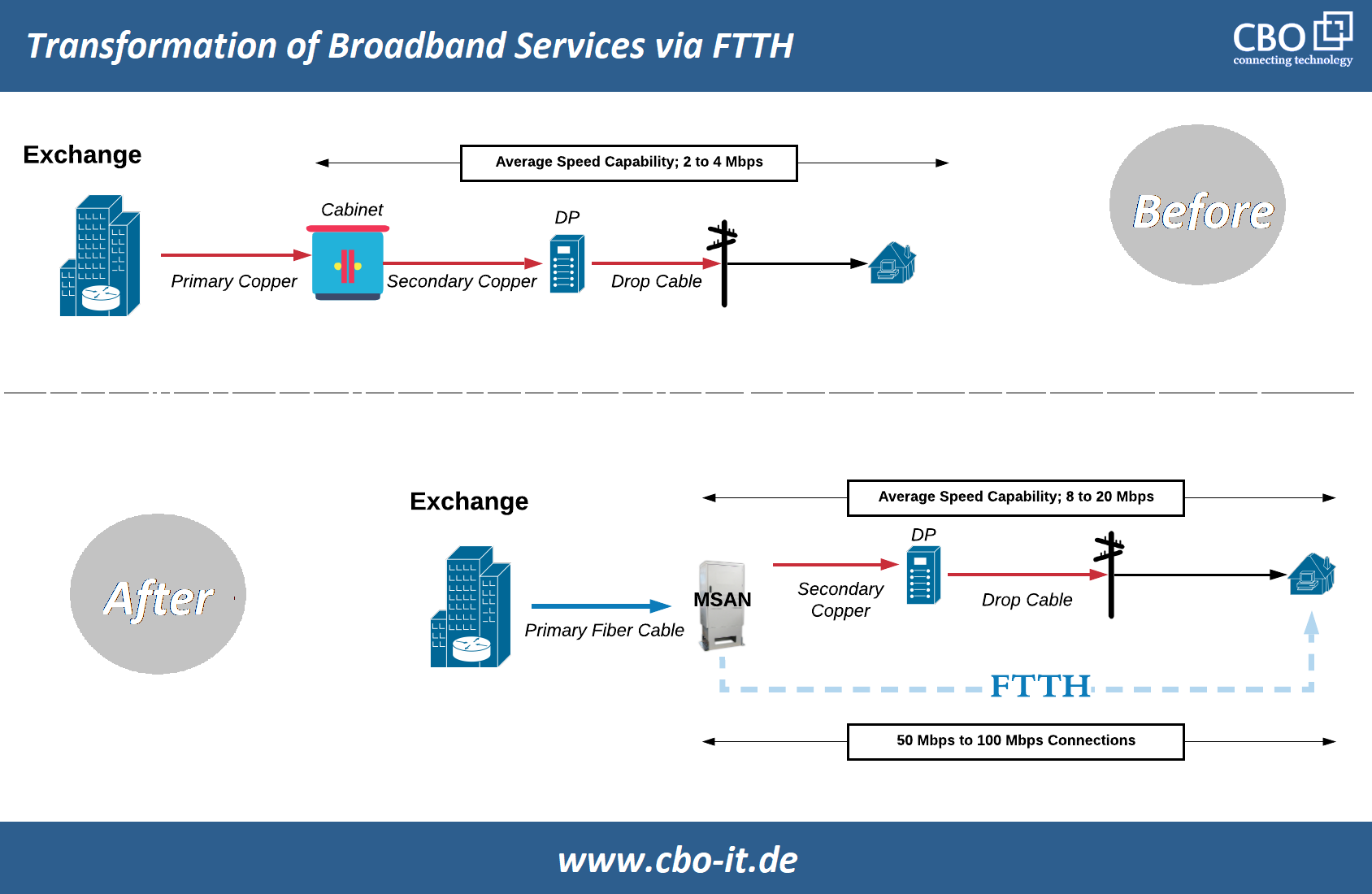
- Currently, there is nothing superior to the optical fiber network when it comes to speed. With a fiber-based internet connection, you will be able to download a 2 hour long HD movies in minutes or seconds.
- According to various market researches, properties with better internet connections are preferred by buyers. It is a known fact that properties with fiber optic internet are usually sold at around 8% more prices as compared to the market value.
- Fiber optic cables are designed to withstand almost all kinds of atmospheric conditions. These cables don’t get affected by electrical interference and you won't require additional grounding cables.
- The ability of fiber to handle the huge flow of data makes it an ideal choice for consumers who opt to triple-play services.
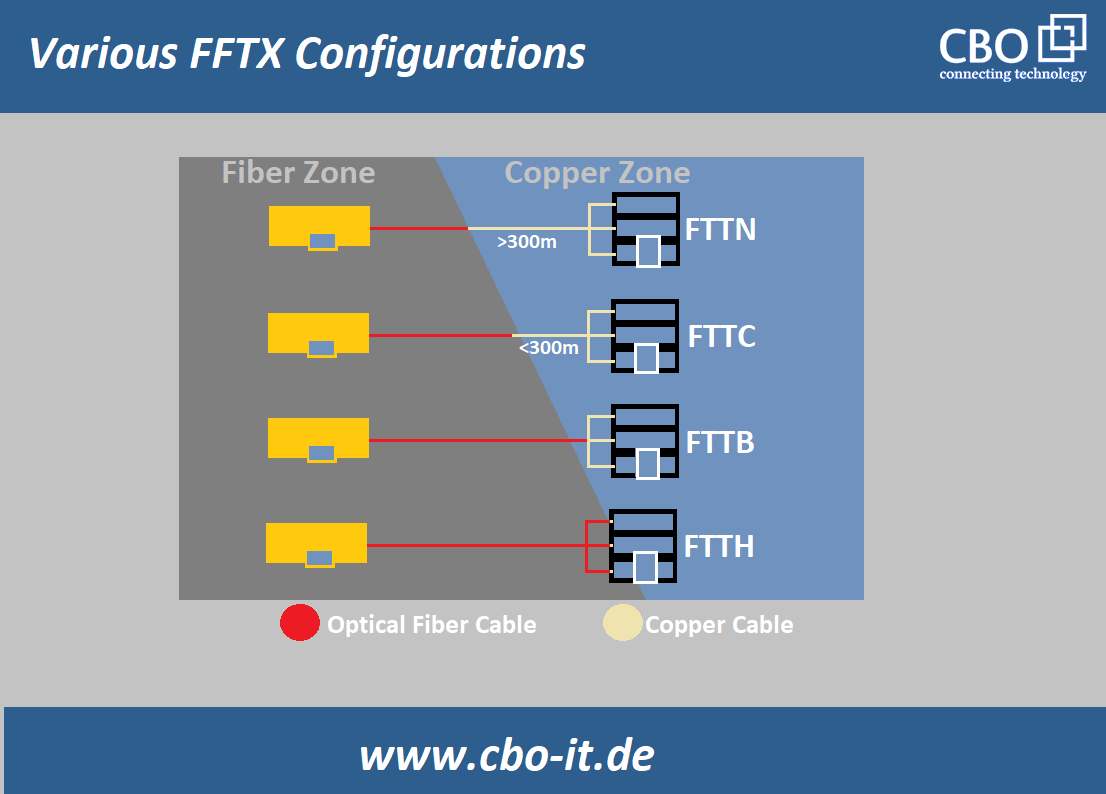
Understanding the abbreviation!
The term FTTx has two parts; FFT is constant and it stands for “fiber-to-the”. Whereas, that “x” actually is a variable and it can be replaced by H, T, and B, etc. In each case, the alphabet used at the place of “x” describes to which extent optical fiber cable is used in last-mile telecommunication or networking. In case if there is an “H” and it is an FFTH configuration that it means that a fiber cable is used to provide connectivity up to consumers home. Similarly in case if there is a “B” and it is an FTTB configuration than it means that a fiber cable is employed for connectivity up to the basement and the remaining part of the connection is completed using a copper cable.
Common FTTX structures (see figure)
Fiber to the home (FTTH)
FFTH is one of the most widely used networking configurations and it is growing at a rapid speed. In this configuration, a fiber cable is utilized for last-mile communication and it is stretched to consumer`s living place such as a building, apartment, office, or home. Point-to-point Ethernet and passive optical networks are commonly used to deliver triple-play-services directly to the subscriber over FFTH networks.
Worldwide penetration and popularity of FTTH networks have resulted in the formation of various FFTH governing bodies and councils. FFTH councils for Asia-Pacific, North America, Europe, and others are working together to keep the entire FFTH network consistent across the world and they have approved definitions for FFTB and FFTH.
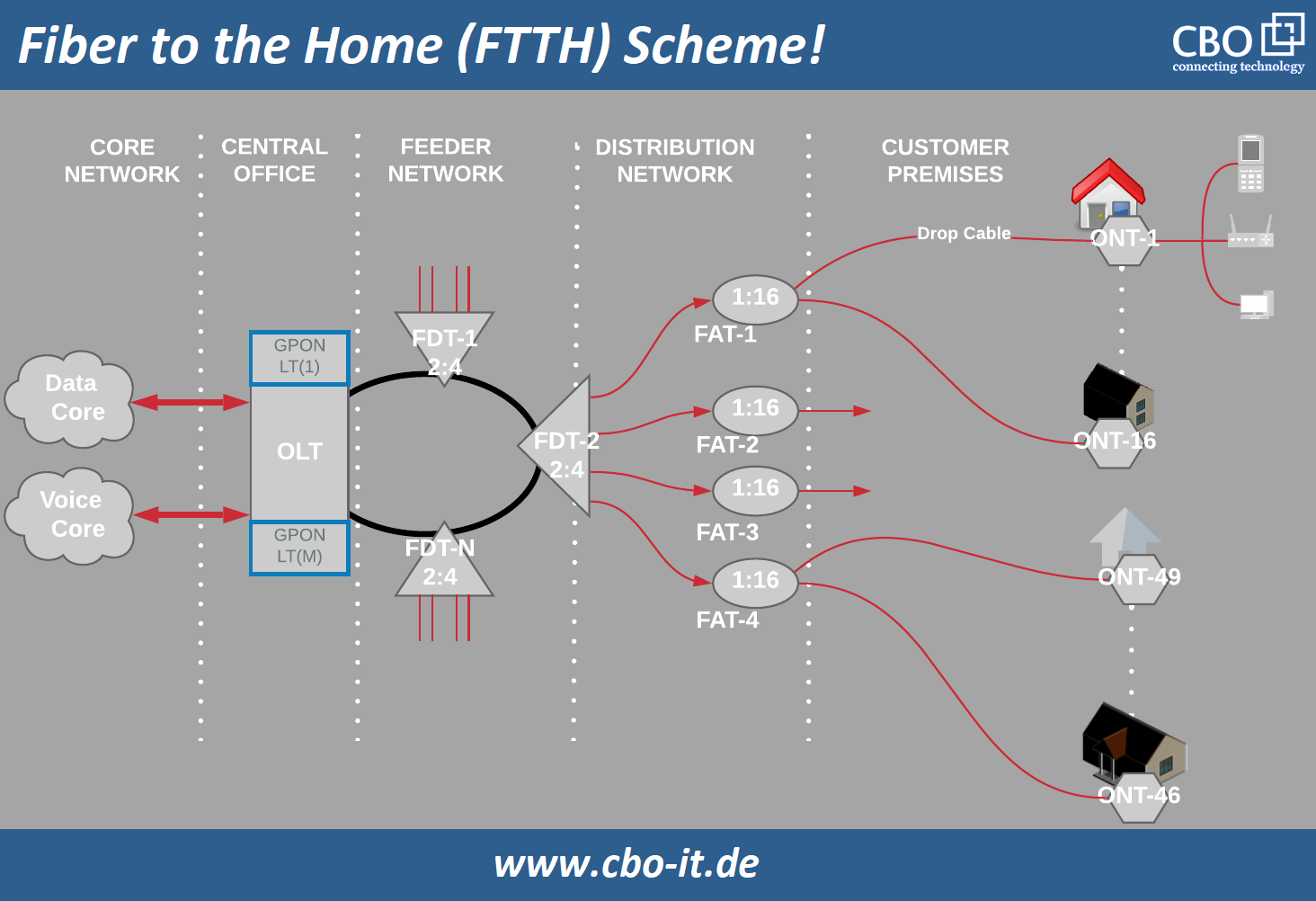
FTTH has various benefits over other access level networking methods as it relies on fiber – a future proof medium of networking. FFTH enables service providers to offer various services such as; telecommunication, internet, and cable TV through a single optical fiber cable. Here, it is important to understand that the FTTH is just one out of various possible FTTX configurations.
Fiber to the building (FTTB)
Fiber to the building is another type of FFTX configuration in which fiber cabling terminates at a central location of a building. Unlike FTTH, FTTB reaches the electrical room or main telecommunication room of the building and the later part of the network relies on a non-optical medium such as copper cables. Thus, the signal is first converted and conveyed to the consumer through wired or wireless channels. FTTB configuration is also called fiber-to-the-basement or fiber-to-the-boundary.
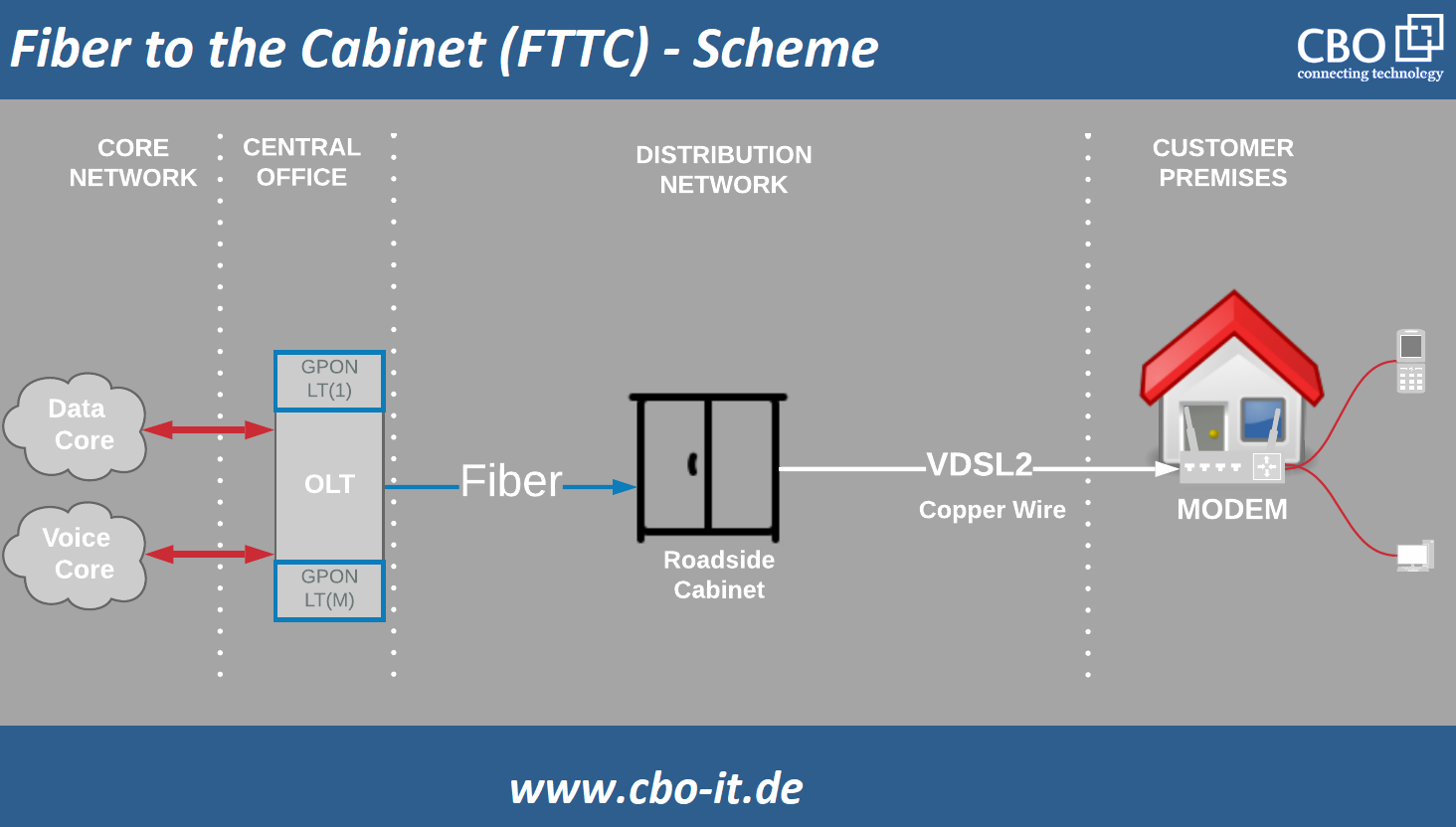
Fiber to the curb or cabinet (FTTC)
Fiber-to-the-cabinet or curb is another very common type of FTTX. In this configuration, an optical fiber cable terminates into a platform that serves multiple subscribers. Each of these subscribers is provided with a connection to this platform via copper or twisted pair cable. In FTTC the “curb” can be considered as a communications shed, closet, or a pole-mounted device. A typical FTTC system should terminate within 300 meters of the subscriber premises equipment. In other words, the length coaxial or twisted pair cable from FTTC termination point to each customer`s equipment should not exceed a distance of 1000 ft. or 300 meters.
Fiber to the Premises (FTTP)
FTTP is not different than FTTB and FTTH. It is a term used in the North American market for referring to Fiber-to-the-home and Fiber-to-the-business. Likewise other FTTX configurations, optical fiber cable are used for last-mile connectivity in FTTP as well. Fiber to the premises is a broader term as it is used to describe networks involving non-residential or commercial buildings as well.
Other FTTX Configurations
Fiber-to-the-x is quite a dynamic technique and we can see its implementation in various ways. The FTTX configurations described above are more common ones. However, in different parts of the world and on different levels more configurations are also possible. Following is a list of various possible FTTX configurations;
- Fiber to the Screen (FTTS)
- Fiber to the Loop (FTTL)
- Fiber to the distribution-point (FTTdp)
- Fiber to the telecom-enclosure (FTTE)
- Fiber to the Zone (FTTZ)
- Fiber to the cell-sire (FTTCS)
- Fiber to the antenna (FTTA)
- Fiber to the Wall (FTTW)
- Fiber to the terminal (FTTT)
- Fiber to the machine (FTTM)
- Fiber to the Factory (FTTF)
- Fiber to the office (FTTO)
- Fiber to the radio (FTTR)
- Fiber to the desk (FTTD)
Conclusion:
FTTX is perhaps the finest last-mile communications approach available as it can be implemented in a variety of configurations. Fiber is widely considered as a future-proof technology as it has the capability of offering high-speed networking with extensive bandwidth.
Most of the ISPs in European and American markets have already started upgrading their networks to incorporate fiber at access levels by using fiber-to-the-home configuration. It is the right time to consider FTTX and especially FTTH as data extensive applications are going to bring a surge in demand in the future.
 English
English
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 Espaniol
Espaniol