Layer 2 switching is a network technology that operates at the Data Link Layer (Layer 2) of the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model. This technology enables network switches to make forwarding decisions based on Media Access Control (MAC) addresses, providing a faster and more efficient way of forwarding data packets within a local area network (LAN).
How Layer 2 Switching Works?
In Layer 2 switching, network switches use a process called MAC learning to build a table that maps MAC addresses to their corresponding network ports. When a switch receives a data packet, it examines the source MAC address of the packet and adds it to its MAC address table, along with the network port that the packet was received on. This process allows the switch to quickly determine the destination network port for subsequent packets with the same source MAC address without needing higher-level routing protocols.
The Basics of MAC Addressing
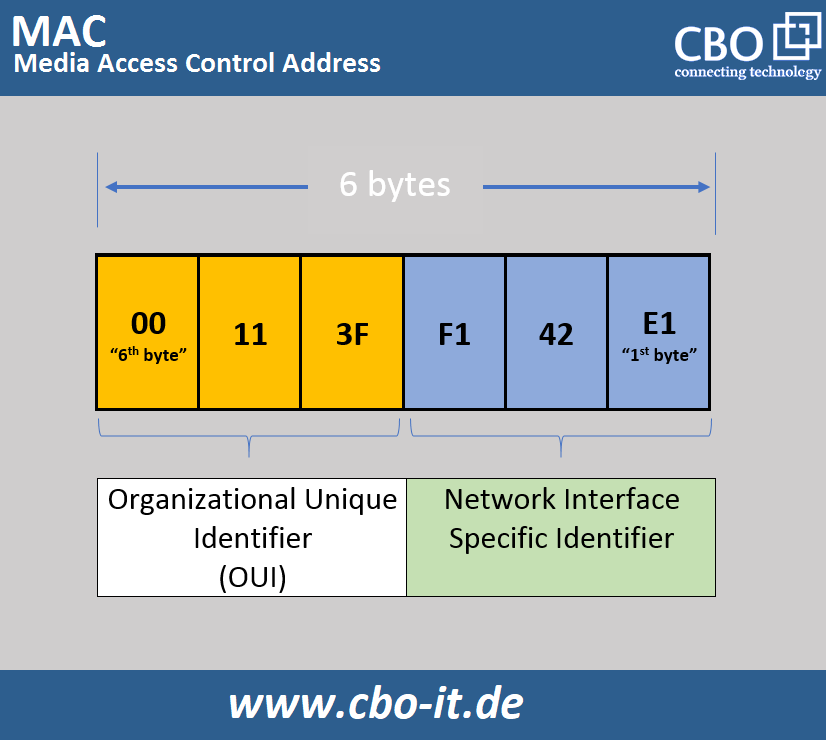
A MAC address is 6 bytes long unique identifier that is physically allocated to a device's network interface controller (NIC). MAC addresses are used for transmissions within a local network segment. MAC addresses are used by layer 2 switching devices, such as switches and bridges, to forward data packets to their intended destination on the local network segment. MAC addresses are typically represented as six sets of two hexadecimal digits, separated by colons or hyphens. They are used in conjunction with other network protocols, such as Ethernet and Wi-Fi.
What is MAC Forwarding?
When a switch receives a data packet, it checks the packet's destination MAC and examines its address table to determine which network port is associated with that address. If the switch has the MAC address in its table, it forwards the packet out of the appropriate network port. If the switch does not have the MAC address in its table, it floods the packet out of all network ports except the one on which it was received to discover the network port associated with the destination MAC address. Once a switch has built its MAC address table, it uses a process called MAC forwarding to determine the network port to which a data packet should be forwarded.
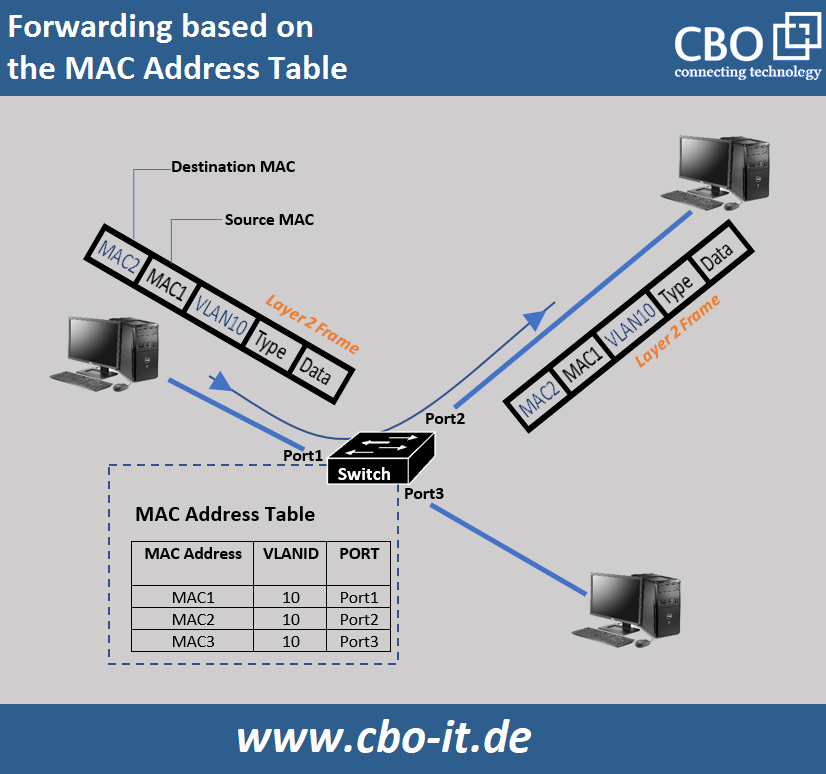
Benefits of Layer 2 Switching
Layer 2 switching provides several benefits over other network technologies, such as routers operating at the OSI model's Network Layer (Layer 3). One of the key benefits is improved performance, as Layer 2 switches can forward data packets much faster than routers can route packets between different networks. Additionally, Layer 2 switching can reduce network congestion by providing more efficient forwarding of data packets within a LAN.
Another benefit of Layer 2 switching is its simplicity. Because Layer 2 switches only make forwarding decisions based on MAC addresses, they do not require complex routing protocols or network configurations. This makes them easier to install and maintain and reduces the risk of configuration errors.
Layer 2 Switching Vs. Routing
Layer 2 switching and routing are different methods of forwarding data packets in computer networks. Here's a summary of each:
Layer 2 switching:
- Operates at OSI model's Layer 2 (Data Link Layer)
- In Layer2 switching, we Use hardware addresses (MACs) to forward data packets to and from the devices on the same local network segment.
- Switches manage and use a MAC address table, allowing them to send packets directly to the intended destination.
- Switches do not analyze packets' contents or make routing decisions based on IP addresses.
- Layer 2 switching is generally faster than routing as it involves fewer data processing and analysis.
Routing:
- Operates at the network layer (Layer 3) of the OSI model.
- It uses IP addresses to forward data packets between devices on different networks.
- Routers maintain a routing table that maps network addresses to outgoing interfaces.
- Routers can make intelligent routing decisions based on network topology and destination IP addresses.
- Routers make routing decisions based on factors such as the shortest path, the fastest path, or the path with the fewest hops.
- Routing involves more processing of packets than layer 2 switching but allows for communication between devices on different networks.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Layer 2 switching is a network technology that provides fast and efficient forwarding of data packets within a LAN. By using MAC learning and MAC forwarding, Layer 2 switches can quickly determine the network port linked with a particular MAC address without the need for complex routing protocols. This simplicity and efficiency make Layer 2 switching a vital technology for modern LANs.
 Espaniol
Espaniol
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 English
English