Concerning communication system, transceiver module temperature is considered as an essential parameter. Operating a transceiver beyond its design temperature range can bring transmission delays, reduced outputs, network breakdown, etc. Consequently, your network may suffer from repeated, undue breakdowns. In this article, we are going to clarify many things about transceivers module temperature.
The transceiver module temperature indicates the available or allowable temperature spread across which a fiber optic transceiver can operate smoothly. Transceiver modules from different vendors may have different temperature ranges, and similar is the case with different types of transceivers. As an example, consider copper modules and optical transceivers. You will always find that the optical transceivers come with a broader range than copper modules. Similarly, the temperature range of the SFP+ module is broader than the SFP module such as:
- 10Gbase-SR - 40°C to 85°C
- 100BASE-SX SFP - 0 to 70°C
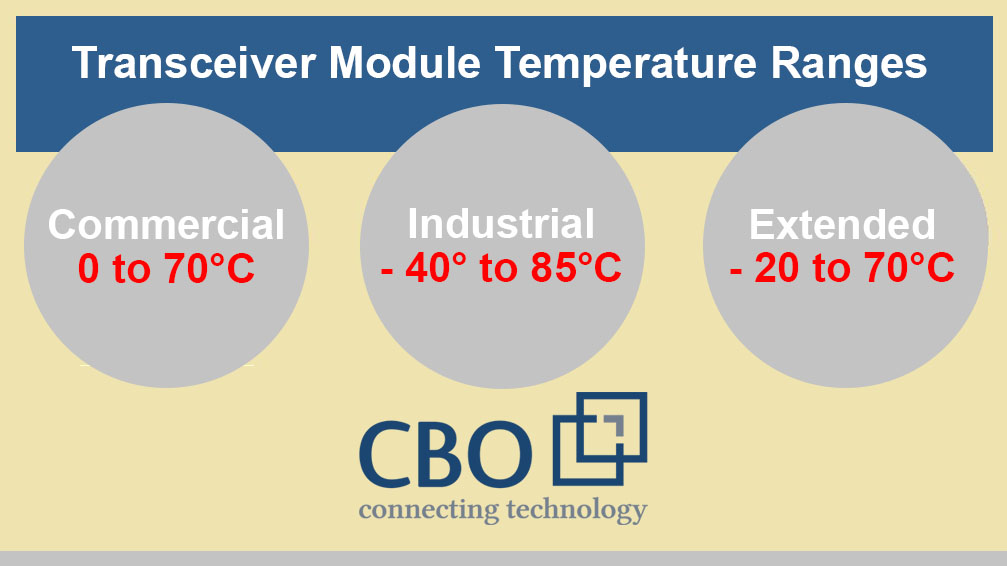
According to the data as provided above; a 10Gbase-SR module can be operated within a temperature range of 40°C to 85°C. Whereas, in 100BASE-SX SFP case module`s operation over a range of 0 to 70°C is possible. Thus, in terms of transceiver module temperature, the 100BASE-SX SFP is more flexible than 10Gbase-SR. Similarly, different modules come with different temperature ranges depending on their built quality, form factor, etc. Conventionally, transceiver modules are graded categorized in three temperature levels:
- 1. Commercial Temperature Range: 0 °C to70°C (denoted by “COM”)
- 2. Extended Temperature Range: -20°C to85°C (denoted by “EXT”)
- 3. Industrial Temperature Range: 40°C to 85°C (denoted by “IND)
Why Is Appropriate Temperature Necessary for Transceiver Modules?
In the case of Higher Temperatures:
Each transceiver module comes with a vendor-defined operating temperature range. The transceiver module will not operate normally in case if its temperature goes too high or too low. In case of higher temperatures, the module will counter a spike in optical power resulting in incorrect reception of signals and disordered operation. In severe operating temperature deviations, the module might burn as well. Thus, temperature monitoring and control system is recommended for real-time monitoring and compensation. Temperature monitoring and control systems ensure that the transceiver is operating with stable luminous power and correct transceiver module extinction ratio.
In Case of Lower Temperatures:
Operating at temperatures lower than the vendor-defined temperatures is something that can result in abnormal and unstable transceiver performance. However, this issue is seldom faced in the data communications industry. Usually, a lower temperature is not encountered because an operating optical fiber system generates heat. Thus, you should avoid the installation of a transceiver in an environment where the temperature stays below 0°C.
Factors Affecting Transceiver Module Temperature
Following are three significant aspects that can affect the transceiver module temperature:
Poor Build Quality
Transceiver modules designed and built poorly with low-quality material often show more sensitivity towards temperature deviations. These modules come with lesser heat dissipation tendency, and thus, their unstable operation cannot be avoided. You can easily avert these issues by choosing high-quality modules.
Harsh Application Environment
Transceiver modules are not designed to be deployed in harsh operating environments such as mountains, deserts, sunlight, etc. Modules installed in offices, data centers, and computer rooms are less likely to malfunction because of operating temperature related issues. On the other hand, modules deployed in harsh and unappropriated operating conditions are more likely to malfunction because of alleviated operating temperatures as their optical sensitivity and optical power may get affected.
Use of Second-Hand Modules
Used or second-handed transceiver modules are generally considered as a cheap alternative of new, high-quality modules. In some case, they might work correctly. However, second-hand transceiver modules are more prone to temperature sensitivity issues as some of their internal parts have already degenerated.
Conclusion:
Maintaining a stable transceiver module temperature is a very critical factor. You can always operate your installed transceiver modules efficiently by maintaining a friendly operating environment. Ensure that you have the right HVAC system emplace. Remember, maintaining a healthy humidity level is also an important thing. CBO offers a broad range of temperature modules designed to operate over a wide temperature range. Our modules can withstand large temperature deviations as they come with a high tolerance level.
 English
English
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 Espaniol
Espaniol