400G ZR or 400ZR is a networking standard designed to enable 400GE transmission over Data Center Interconnect links. 400ZR supports up to 80 km links and it utilizes a technology called “Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing”. 400G ZR tends to provide long-term, single-carrier 400G implementation through dual-polarization 16 QAM at around 60 gigabaud where 16 QAM stands for 16-state Quadrature Amplitude Modulation.
The 400ZR project is a venture of the Optical Interconnect Forum (OIF) and its main purpose is;
- Reduction in complexity and cost of high-speed, high-bandwidth data center interconnects
- To provide better interoperability between different optical transceivers manufacturers
To cater to intensive cloud services and other data center processing and storage needs, the data center structure has become highly decentralized, complicated, and difficult to manage. IoT applications such as Artificial Intelligence require high-bandwidth and low-latency network architectures to effectively handle a high volume of data transfer between machines and servers. To ensure optimum performance of IoT applications the maximum length of fiber between different data centers must not exceed 100 kilometers. Here comes the concept of cluster-based interconnection between data centers and 400G ZR.
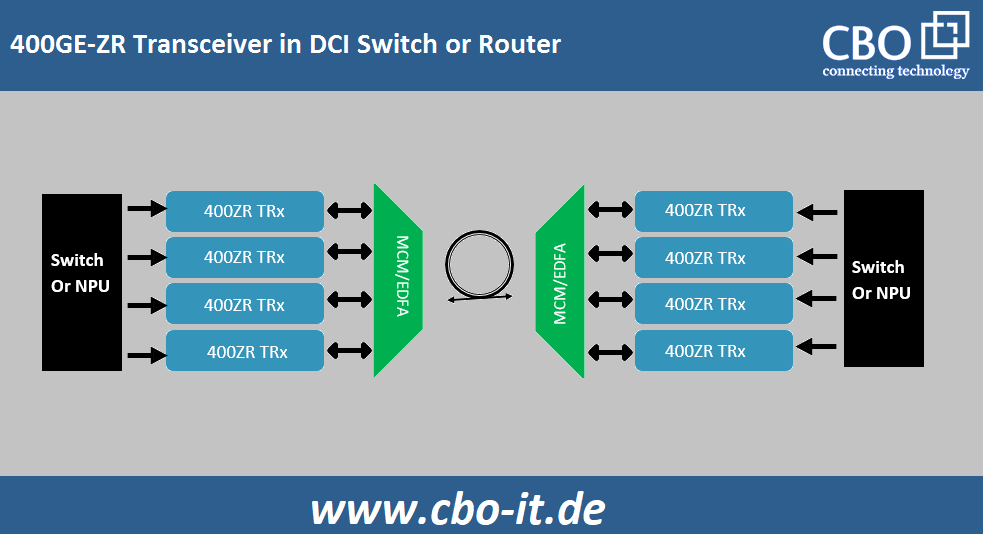
400G ZR incorporates a technology-oriented solution for high-volume data transmission which could par the performance of the 400GE switch port. It employs an exceptional design of sophisticated coherent optical technology for compact, pluggable form factor modules.
By now, we don’t have a 400G ZR product form-factor mentioned in the “Implementation Agreement”. However, networking hardware vendors have agreed upon a common set of the specification to suit the solution. These form factors are separately defined by “Multi-Source Agreement” bodies as is the case with other transceivers such as OSFP and QSFP-D which can be plugged into compatible ports. Thus, it can be concluded that the upcoming 400G ZR solutions will offer interoperability because the OIF and 400ZR MSAs are industry-wide organizations. The interoperability of the upcoming 400G ZR solutions offers multiple benefits of simplified deployment and supply chain management.
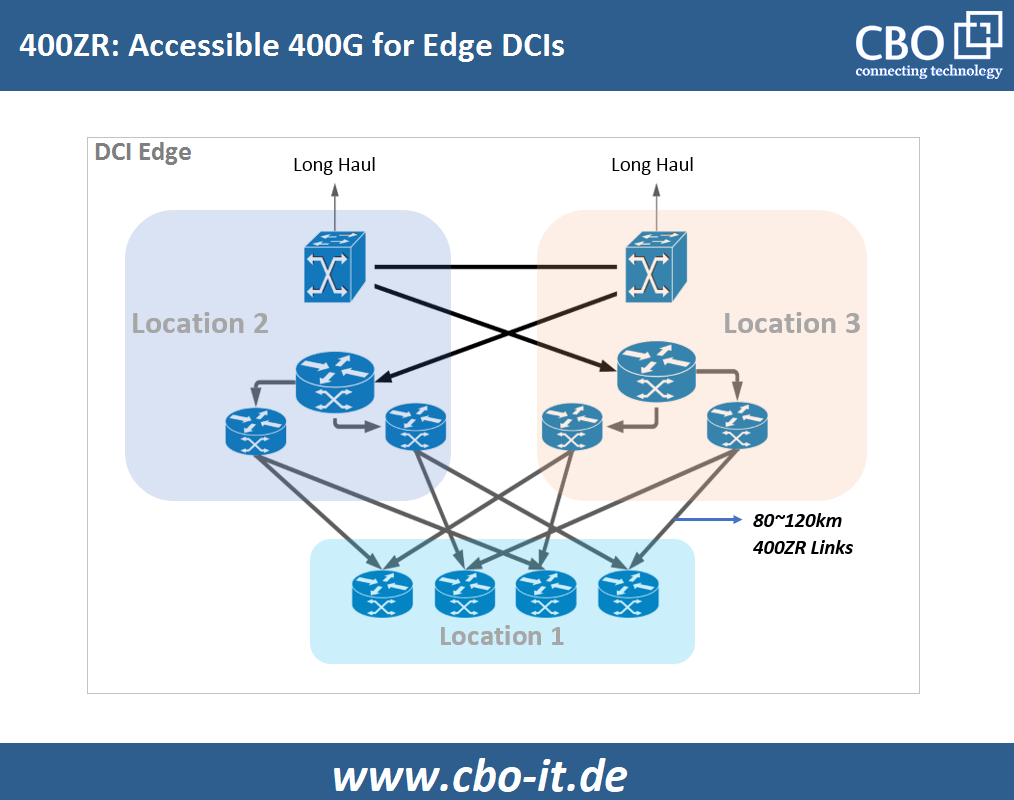
400G ZR+ or 400ZR+
The coherent, pluggable 400ZR solution will support both multi-vendor interoperability and 400G Ethernet interconnection. However, this solution is not a potent choice for the next-generation metro and regional networks where transmission distances longer than 80 kilometers are required with a capacity of 400 Gb/s. For such conditions, 400G ZR+ or 400ZR+ is proposed. It is anticipated that the 400ZR+ will further enhance modularity by supporting multiple channel capabilities based on coverage requirements and compatibility with already installed optical metro hardware. With 400ZR+ both the line capacity and transmission distance could be assured.
What Impacts Will 400G ZR Bring?
Factually speaking 400G ZR technology is still in its development phase. However, it is widely considered that this technology will bring a substantial impact on multiple industries including;
- Telecommunications
- Hyperscale data centers
- Distributed campus networks
Role of 400G ZR for Hyperscale Data Centers and Cloud Computing
The development of the 400G ZR and DCI would help with the extensively growing demand for cloud computing and hyperscale data centers. 400G ZR has the resources to cope with the exponential growth of applications including IoT devices, cloud services, and streaming video. Further development of 400G ZR will play a complementary role in the enhancement of ever-growing, bandwidth-hungry applications.
Role of 400G ZR in Distributed Data Center Interconnects
As is established above, 400G ZR technology will have a positive impact on high-bandwidth distributed data center interconnects. 400G ZR-based interconnecting links between distributed data centers will enable robust communication, balancing of workloads and these links will also bring straightforward expansion in data center capacity.
Role of 400G ZR in Telecommunications
400G ZR standard will enable telecommunication service providers to backhaul residential traffic. 400G ZR can raise the operating range of high loss spans while running at 200 Gb/s through QPSK modulation and 64 Gbaud signaling. For 5th generation networks, 400ZR make available mobile backhaul by combining multiple streams of 25 Gb/s. 400ZR will bring a positive impact on 5G emerging markets and applications.
400ZR+/400ZR- Will Offer Greater Convenience
The 400ZR transceiver is expected to support various modes to enhance the span of addressable applications. These modes include 400ZR+ and 400ZR-. Here, “+” indicates that the module tends to use more powerful signaling technologies by consuming up to or more than 15 watts of power as defined by IA. Whereas, “-” suggests that the transceiver supports lo=speed modes such as 100G, 300G, and 200G, which offers more flexibility to network operators.
Conclusion
400G ZR is still in its development phase but it is widely anticipated that this new technology will bring a pleasant impact on data center interconnects for extensive networking applications. The 400ZR is intended to minimize the cost and complication of data center interconnects. In the future, we will be able to find interoperable, compact 400G ZR modules widely across the market.
 English
English
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 Espaniol
Espaniol