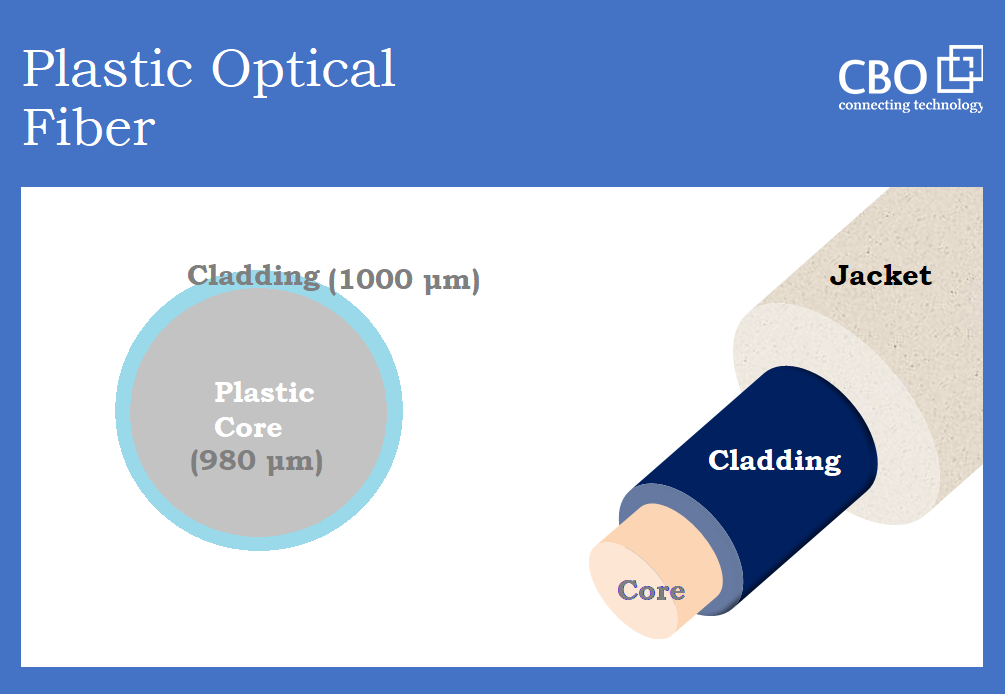
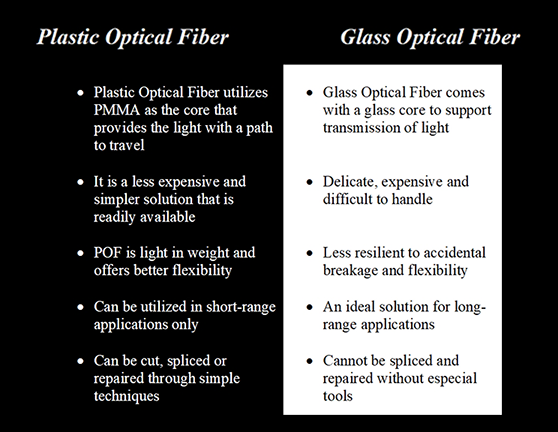
We always turn to optical fibers to address our high bandwidth networking requirements. Generally speaking, many don’t know much about the existence of plastic optical fiber. Both glass fiber and plastic fiber have different advantages and shortcomings. Today, we are going to provide our users with some vital information in this regard.
Glass Optical Fiber – a Quick Overview
A few decades back no one could have ever imagined about the possibility of transmitting valuable information via glass – an element abundantly available. Later, someone came ahead with this brilliant idea and proposed light as a potent carrier of data. Subsequently, we saw dramatic development in this field and optical fiber became the most desired medium for digital communication.
In reality, glass optical fibers are nothing but bundles of tiny glass strands – and that’s all. Whatever other stuff we found in our optical fiber cables such as; cladding and sheathing etc. are provided for reinforcement only. Glass has an inherent property of refracting light and this is how it works. In glass optical fiber we achieve complete internal refraction to keep the light enclosed and moving along the glass made cable. In optical fiber cables, the core of the fiber strands is surrounded by cladding media. The sole purpose of the cladding is to reject any refract of light. Thus, the light traveling through the core of the cable remains entrapped. Here, it is important to understand that a glass with a poor refractive index is utilized in the construction of the cladding.
In optical fiber-based communication systems specially designed networking hardware is utilized. There are different communication standards and protocols available for networking over optical fiber cables. Different grades and types of cables are available for various kinds of short, medium and long-distance applications. Wondering about the source of light that is used for signaling purposes in optical fiber networking? Well, it’s not a big deal – don’t we have such a shining sun available? Wait here. There is a problem with the Sun as it cannot provide light to every continent simultaneously. So, it cannot be the Sun. In optical fiber networking systems, we use specially designed LEDs or photoelectric sensors to provide us with the light to travel across the optical fiber cable.
These light sources are connected and controlled by communication controllers which turn the light source on and off in a pattern to convert the supplied digital data into light signals. For a “0” the light source will be turned “Off” and for a “1” the source will be turned “On”. Sounds simple right? This is how it works. Now, let us proceed with some of the biggest benefits of using glass optical fiber as our digital communications medium.
Glass Optical Fiber – Benefits
Glass optical fiber is a tremendous choice available for a variety of applications and networking requirements. Glass is one of the most abundant, naturally occurring elements –so we don’t have to worry about its availability. Networking over glass optical fiber has become a global phenomenon and you can easily acquire the required parts and components according to your specific needs and applications. Moreover, glass optical fiber cables are available in different types with different data-carrying capabilities. Another great advantage of going with glass optical fiber is its tendency to withstand harsh operating environments. Unlike plastic, you can easily deploy an optical fiber cabling nearby a furnace or heat waves emitting equipment. The inherited light-transmitting ability of glass makes it an ideal choice for long haul applications. Moreover, glass optical fiber can work with both; infrared light and visible light. As we have mentioned about high-temperature applications glass fiber optic is suitable for extremely low-temperature areas as well.
Basics of Plastic Optical Fiber
Well, there is not much difference between glass optical fiber and plastic optical fiber when it comes to their construction and the main working principles. In a plastic optical fiber, glass is replaced by plastic – that’s all. In these cables, we get a core made of tiny plastic strands reinforced and surrounded with a different grade plastic cladding. However, the thing that remains unchanged is the involvement of light. To make it clear just imagine that we are talking about the same car but different roads. Unlike glass that is a naturally occurring element, plastic is produced synthetically. We cannot manipulate the characteristics of glass but yes! We can produce networking grade plastic to get the best possible results. Plastic Optical Fiber is generally considered as “consumer” optical fiber because of its cheaper price. This kind of optical fiber is widely used in home networks, digital home appliances, and other short-distance, low-speed applications. The distortion and attenuation characteristics of plastic optical fiber make it a less preferred choice for long-distance, high-speed and bandwidth extensive applications.
Technically, both the glass and plastic optic fiber work on a similar phenomenon. In plastic optical fiber cables, plastic made core is utilized for the transmission of data. Whereas, specially formulated fluorinated polymers are used as the cladding material in these cables.
Plastic Optical Fiber – Benefits
When it comes to cost and flexibility – plastic optical fiber is matchless. Optical cables designed with a plastic core and cladding are available at a much cheaper price in comparison to the cables which use glass core and cladding. Today, you can easily find a broad range of accessories, connectors and other components for plastic optical fibers on the market. So, the availability of parts and scalability is not an issue. As far as the matter of safety is concerned, plastic optical fiber is a much better option because it uses harmless red or green light, visible to the naked eye. Another great benefit of using plastic optical fiber is its higher tendency to withstand bends, vibration, and shock. Handling and installation of the plastic optical fiber require no special training, tools, and techniques. You can use a simple pair of scissors to cut a plastic optical fiber cable and it will when you plug it back.
Glass vs. Plastic Optical Fiber – Conclusion
Glass optical fiber and plastic optical fiber are two wonderful networking options available. On one hand, we have plastic optical fiber that is cheaper and easy to handle. However, it is not a viable option offer for long-haul applications.
Yes! Plastic optical fiber is a great choice for short-range connectivity. On the other hand, we have time-tested glass optical fiber. Glass optical fiber is a universal solution available for both; short-range and long-range applications.
So, you should consider glass fiber cables when a long-range, fast-speed connection is intended because plastic optical fiber is designed to provide bit rates up to 10 Gbps only.
 English
English
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 Espaniol
Espaniol